El asList() mètode de java.util.Arrays class s'utilitza per retornar una llista de mida fixa recolzada per la matriu especificada. Aquest mètode actua com a pont entre les API basades en matrius i les basades en col·leccions , en combinació amb Collection.toArray(). La llista retornada és serializable i implementa RandomAccess.
Consell: Això s'executa en temps O(1).
Sintaxi:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Paràmetres: Aquest mètode pren el matriu a que cal convertir en una llista. Aquí... es coneix com vararg que és una matriu de paràmetres i funciona de manera similar a un paràmetre de matriu d'objectes.
angles adjacents
Nota especial: El tipus de matriu ha de ser una classe Wrapper (Integer, Float, etc.) en cas de tipus de dades primitius (int, float, etc), és a dir, no podeu passar int a[] però podeu passar Integer a[]. Si passeu int a[], aquesta funció retornarà una llista i no una llista, ja que l'autoboxing no passa en aquest cas i int a[] s'identifica com a objecte i es retorna una matriu List of int, en lloc de list. de nombres enters, que donarà error en diverses funcions de col·lecció.
Valor de retorn: Aquest mètode retorna a vista de llista de la matriu especificada.
Exemple 1:
Java
ordre per sql aleatori
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Sortida
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Exemple 2:
Java
Edith Mack Hirsch
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
tutorial del llenguatge de programació java
>
>Sortida
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Exemple 3:
Java
8 a 1 multiplexor
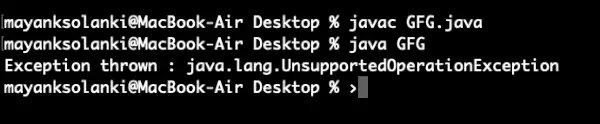
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Sortida: