 #practiceLinkDiv { mostrar: cap !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { mostrar: cap !important; }L'algorisme d'eliminació inversa està estretament relacionat amb algorisme de Kruskal . En l'algorisme de Kruskal el que fem és: Ordenar les arestes per ordre creixent dels seus pesos. Després d'ordenar, triem les vores una per una en ordre creixent. Inclouem l'aresta seleccionada actual si en incloure-la a l'arbre spanning no formem cap cicle fins que hi hagi arestes V-1 a l'arbre spanning on V = nombre de vèrtexs.
A l'algorisme d'eliminació inversa ordenem totes les vores decreixent ordre dels seus pesos. Després d'ordenar, escollim les vores d'una en una en ordre decreixent. Nosaltres incloure la vora triada actual si l'excloure de la vora actual provoca la desconnexió al gràfic actual . La idea principal és eliminar la vora si la seva supressió no comporta la desconnexió del gràfic.
classe de cadena java
L'algoritme:
- Ordena totes les arestes del gràfic en ordre no creixent dels pesos de les arestes.
- Inicieu MST com a gràfic original i elimineu les vores addicionals mitjançant el pas 3.
- Trieu la vora més gran de les vores restants i comproveu si suprimir la vora desconnecta el gràfic o no .
Si es desconnecta, no suprimirem la vora.
En cas contrari, eliminem la vora i continuem.
Il·lustració:
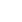
Entenem-ho amb el següent exemple:
Si suprimim la vora de pes més alta del gràfic de pes 14 no es desconnecta, així que l'eliminem.
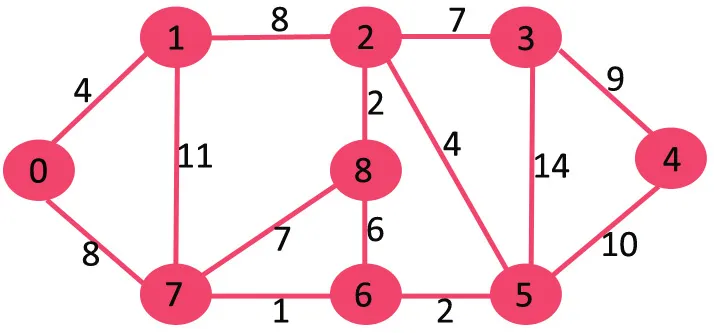
A continuació, suprimim 11 ja que suprimir-lo no desconnecta el gràfic.
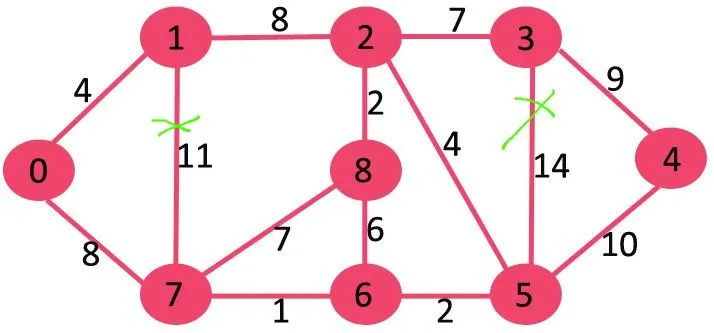
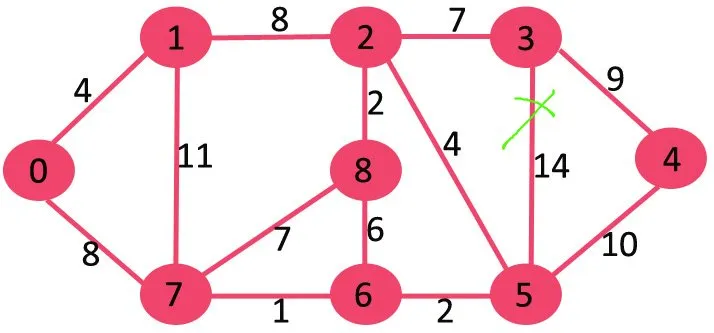
A continuació, suprimim 10 ja que suprimir-lo no desconnecta el gràfic.

El següent és el 9. No podem suprimir el 9, ja que suprimir-lo provoca la desconnexió.

Continuem d'aquesta manera i les vores següents romanen a l'MST final.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Nota: En cas de vores del mateix pes, podem escollir qualsevol vora de les vores del mateix pes.
Pràctica recomanada Algorisme d'eliminació inversa per a l'arbre d'abast mínim Prova-ho!Implementació:
C++// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #include
// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.*; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { int u v w; Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.w = w; this.v = v; } public int compareTo(Edge other) { return (this.w - other.w); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<Integer>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; @SuppressWarnings({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v boolean[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections.sort(edges); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST System.out.println('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges.get(i).u; int v = edges.get(i).v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].remove(adj[u].indexOf(v)); adj[v].remove(adj[v].indexOf(u)); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].add(v); adj[v].add(u); // This edge is part of MST System.out.println('(' + u + ' ' + v + ')'); mst_wt += edges.get(i).w; } } System.out.println('Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; GFG g = new GFG(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
# Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self v): # No. of vertices self.v = v self.adj = [0] * v self.edges = [] for i in range(v): self.adj[i] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self u: int v: int w: int): self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list. self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list. self.edges.append((w (u v))) def dfs(self v: int visited: list): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self.adj[v]: if not visited[i]: self.dfs(i visited) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected(self): visited = [False] * self.v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self.dfs(0 visited) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range(1 self.v): if not visited[i]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST(self): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self.edges.sort(key = lambda a: a[0]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print('Edges in MST') # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range(len(self.edges) - 1 -1 -1): u = self.edges[i][1][0] v = self.edges[i][1][1] # Remove edge from undirected graph self.adj[u].remove(v) self.adj[v].remove(u) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self.connected() == False: self.adj[u].append(v) self.adj[v].append(u) # This edge is part of MST print('( %d %d )' % (u v)) mst_wt += self.edges[i][0] print('Total weight of MST is' mst_wt) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph(V) # making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4) g.addEdge(0 7 8) g.addEdge(1 2 8) g.addEdge(1 7 11) g.addEdge(2 3 7) g.addEdge(2 8 2) g.addEdge(2 5 4) g.addEdge(3 4 9) g.addEdge(3 5 14) g.addEdge(4 5 10) g.addEdge(5 6 2) g.addEdge(6 7 1) g.addEdge(6 8 6) g.addEdge(7 8 7) g.reverseDeleteMST() # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable<Edge> { public int u v w; public Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.v = v; this.w = w; } public int CompareTo(Edge other) { return this.w.CompareTo(other.w); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<int>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; public Graph(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new List<int>[ v ]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); edges = new List<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].Add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].Add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.Add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v bool[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected() { bool[] visited = new bool[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges.Sort(); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST Console.WriteLine('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges[i].u; int v = edges[i].v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].Remove(v); adj[v].Remove(u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].Add(v); adj[v].Add(u); // This edge is part of MST Console.WriteLine('({0} {1})' u v); mst_wt += edges[i].w; } } Console.WriteLine('Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main(string[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; Graph g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
// Javascript program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { // Constructor constructor(V) { this.V = V; this.adj = []; this.edges = []; for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // function to add an edge to graph addEdge(u v w) { this.adj[u].push(v);// Add w to v’s list. this.adj[v].push(u);// Add w to v’s list. this.edges.push([w [u v]]); } DFS(v visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; for (const i of this.adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) { this.DFS(i visited); } } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false isConnected() { const visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { visited[i] = false; } // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex this.DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (let i = 1; i < this.V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { return false; } } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not reverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost this.edges.sort((a b) => a[0] - b[0]); let mstWt = 0;// Initialize weight of MST console.log('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (let i = this.edges.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { const [u v] = this.edges[i][1]; // Remove edge from undirected graph this.adj[u] = this.adj[u].filter(x => x !== v); this.adj[v] = this.adj[v].filter(x => x !== u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (!this.isConnected()) { this.adj[u].push(v); this.adj[v].push(u); // This edge is part of MST console.log(`(${u} ${v})`); mstWt += this.edges[i][0]; } } console.log(`Total weight of MST is ${mstWt}`); } } // Driver code function main() { // create the graph given in above figure var V = 9; var g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4); g.addEdge(0 7 8); g.addEdge(1 2 8); g.addEdge(1 7 11); g.addEdge(2 3 7); g.addEdge(2 8 2); g.addEdge(2 5 4); g.addEdge(3 4 9); g.addEdge(3 5 14); g.addEdge(4 5 10); g.addEdge(5 6 2); g.addEdge(6 7 1); g.addEdge(6 8 6); g.addEdge(7 8 7); g.reverseDeleteMST(); } main();
Sortida
Edges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37
Complexitat temporal: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) on E és el nombre d'arestes.
cadena a enter en java
Complexitat espacial: O(V+E) on V és el nombre de vèrtexs i E és el nombre d'arestes. Estem utilitzant una llista d'adjacència per emmagatzemar el gràfic, de manera que necessitem espai proporcional a O(V+E).
Notes:
- La implementació anterior és una implementació senzilla/naïf de l'algorisme de supressió inversa i es pot optimitzar a O(E log V (log log V)3) [Font: Una setmana ]. Però aquesta complexitat de temps optimitzada encara és menor Prim i Kruskal Algorismes per a MST.
- La implementació anterior modifica el gràfic original. Podem crear una còpia del gràfic si cal conservar el gràfic original.
Crea un qüestionari
