De vegades, hem de comprovar el tipus de dades d'una variable per calcular les dades perquè podem realitzar l'operació lògica amb el mateix tipus de variables. Per comprovar el tipus de dades, utilitzem el mètode getClass() i getSimpleName() per obtenir la classe i el seu nom respectivament. En aquesta secció, parlarem Com comprovar el tipus de dades a Java?
guineu o llop
Implementem el codi per obtenir els tipus de dades de les variables. Primer prenem l'entrada de l'usuari i després trobem el tipus de dades de les variables en què s'emmagatzemarà l'entrada de l'usuari.
CheckDataTypeExample.java
import java.util.*; // create class CheckDataTypeExample to check the datatype of the variable public class CheckDataTypeExample { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare variables int intData; char charData; // create Scanner class object to take input from user Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take input from the user to initialize variables System.out.println('Enter a String value:'); String str = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter Integer value:'); intData = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println('Enter Character value:'); charData = sc.next().charAt(0); // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // show datatypes of variables by using getClass() and getSimpleName() methods System.out.println(intData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)intData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(charData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)charData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(str + ' is of type ' + str.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } Sortida:
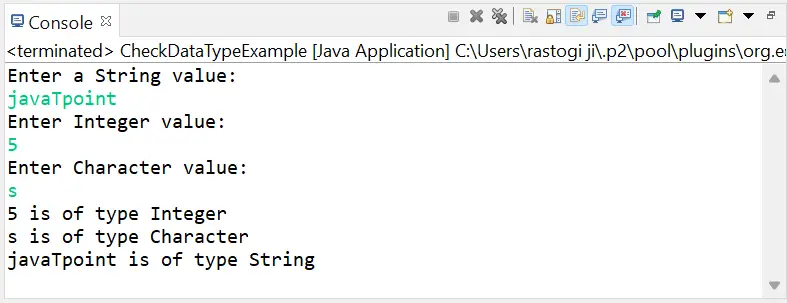
Ara, tenim un mètode especial, és a dir, getType() proporcionat per java.lang.reflect.Field i classes de caràcters. Entenem el mètode getType() d'ambdues classes una per una.
Field.getType()
El getType() mètode de el camp class s'utilitza per obtenir el tipus de camp definit per l'objecte Field. El valor de retorn ens ajuda a identificar el tipus de camp.
Sintaxi:
La sintaxi de la getType() mètode és el següent:
public String getType()
Paràmetre: No accepta cap argument com a paràmetre.
Devolucions: Retorna un objecte de classe que ens ajuda a identificar el tipus de camp.
Prenguem un exemple del mètode getType() i entenem com funciona:
GetTypeExample1.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample1 to get the type of the Field public class GetTypeExample1 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //get the name field object by using getField() method Field nameField = Student.class.getField('name'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field Class value = nameField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the name field is ' + value); //get the totalMarks field object by using getField() method Field marksField = Student.class.getField('totalMarks'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of totalMarks field value = marksField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the totalMarks field is ' + value); //get the totalFees field object by using getField() method Field feesField = Student.class.getField('totalFees'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field value = feesField.getType(); // print the type of the totalFees field System.out.println('The type of the totalFees field is ' + value); } } // create a simple student class class Student { // declare and initialize variables public static String name = 'John'; public static double totalMarks = 380; public static float totalFees = 3413.99f; // getter for student name public static String getName() { return name; } // setter for student name public static void setName(String stdName) { name = stdName; } // getter for totalMarks public static double getTotalMarks() { return totalMarks; } // setter for totalMarks public static void setMarks(double marks) { totalMarks = marks; } // getter for totalFees public static float getTotalFees() { return totalFees; } // setter for totalFees public static void setFees(float fees) { totalFees = fees; } } Sortida:
conversió de cadena a enter en java

Utilitzant el mètode Field.getType().
El getType() mètode de Personatge class s'utilitza per obtenir la categoria general del caràcter donat. El mètode getType() inclou dues variacions basades en el paràmetre, és a dir, Character.getType(char ch) i Character.getType(int codePoint) .
El mètode getType() que pren el caràcter com a paràmetre no pot gestionar els caràcters addicionals, mentre que el mètode getType() que pren un int com a paràmetre pot gestionar els caràcters addicionals.
Sintaxi:
El getType() mètode de la Personatge class té la sintaxi següent:
flotar a la corda
public static int getType(char ch) public static int getType(int codePoint)
Paràmetre: La primera variació del mètode getType() accepta un paràmetre de tipus char i la segona variació del mètode accepta un paràmetre de tipus int, és a dir, codePoint.
Devolucions: Tots dos mètodes retornen un valor enter que indica la categoria general de caràcter.
Prenguem un exemple del mètode getType() i entenem com funciona:
GetTypeExample2.java
// import required classes and package if any // create class GetTypeExample2 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample2 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set ch1, ch2 in CharData CharData.setChar1('C'); CharData.setChar2('%'); // use getter to get char1 and char2 char char1 = CharData.getChar1(); char char2 = CharData.getChar2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(char1); int val2 = Character.getType(char2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +char1 + ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +char2 + ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CharData class class CharData { // declare variables of type char static char ch1, ch2; // getter for ch1 public static char getChar1() { return ch1; } // setter for ch1 public static void setChar1(char ch) { ch1 = ch; } // getter for ch2 public static char getChar2() { return ch2; } // setter for ch2 public static void setChar2(char ch) { ch2 = ch; } } Sortida:

GetTypeExample3.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample3 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample3 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set code1, code2 in CodePoint CodePoint.setCodePoint1(0x0037); CodePoint.setCodePoint2(0x016f); // use getter to get code1 and code2 int code1 = CodePoint.getCodePoint1(); int code2 = CodePoint.getCodePoint2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(code1); int val2 = Character.getType(code2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +code1+ ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +code2+ ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CodePoint class class CodePoint { // declare variables of type int static int codePoint1, codePoint2; // getter for codePoint1 public static int getCodePoint1() { return codePoint1; } // setter for codePoint1 public static void setCodePoint1(int code1) { codePoint1 = code1; } // getter for codePoint2 public static int getCodePoint2() { return codePoint2; } // setter for codePoint2 public static void setCodePoint2(int code2) { codePoint2 = code2; } } Sortida:

