Inicialment, donat un conjunt buit i diverses consultes sobre cadascuna possiblement dels tipus següents:
- Inseriu "X" mitjançant l'actualització (1 0 10^6 x 1). Tingueu en compte que l’arrel de l’arbre es passa l’índex d’inici es passa com a 0 i l’índex final com a 10^6 de manera que tots els intervals que tinguin X s’actualitzin.
- Eliminar "X" es fa mitjançant l'actualització (1 0 10^6 x -1). Tingueu en compte que l’arrel de l’arbre es passa l’índex d’inici es passa com a 0 i l’índex final com a 10^6 de manera que tots els intervals que tinguin X s’actualitzin.
Exemple:
Input : Insert 1 Insert 4 Insert 7 Median Output : The first three queries should insert 1 4 and 7 into an empty set. The fourth query should return 4 (median of 1 4 7).
Per a propòsits expositius, suposem el següent, però aquests supòsits no són les limitacions del mètode que es discuteix aquí:
1. En qualsevol cas, tots els elements són diferents que no es produeix cap d'ells més d'una vegada.
2. La consulta "mediana" només es fa quan hi hagi un nombre estrany d'elements al conjunt. (Haurem de fer dues consultes al nostre arbre del segment en cas de nombres parells)
3. Els elements del conjunt oscil·len d’1 a +10^6.
Mètode 1 (ingenu)
En la implementació ingènua podem fer les dues primeres consultes a O (1), però la darrera consulta a O (Max_Elem) on Max_elem és l’element màxim de tots els temps (inclosos elements suprimits).
Suposem una matriu Comte [] (de mida 10^6 + 1) Per mantenir el recompte de cada element al subconjunt. A continuació, es mostren algoritmes simples i explicatius per a les 3 consultes:
Inseriu la consulta X:
count[x]++; if (x > max_elem) max_elem = x; n++;
Suprimeix la consulta X:
if (count[x] > 0) count[x]--; n--;
Consulta mediana:
sum = 0; i = 0; while( sum <= n / 2 ) { i++; sum += count[i]; } median = i; return median; Il·lustració del recompte de matrius [] que representa el conjunt {1 4 7 8 9} L'element mitjà és "7":
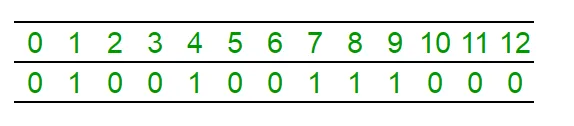
La consulta "mitjana" té la intenció de trobar la (n + 1)/2 "1" a la matriu en aquest cas 3er "1"; Ara fem el mateix mitjançant un arbre de segments.
Mètode 2 (mitjançant Arbre del segment Que)
Fem un arbre del segment Per emmagatzemar la suma d’intervals on un interval [a b] representa el nombre d’elements presents al conjunt actualment en el rang [a b]. Per exemple, si considerem que la consulta d’exemple anterior (3 7) Retorna 2 consulta (4 4) Retorna 1 consulta (5 5) Retorna 0.
Les consultes d’inserció i suprimir són senzilles i ambdues es poden implementar mitjançant l’actualització de funcions (int x int dif) (afegeix “dif” a l’índex “x”)
Algorisme
// adds ‘diff’ at index ‘x’ update(node a b x diff) // If leaf node If a == b and a == x segmentTree[node] += diff // If non-leaf node and x lies in its range If x is in [a b] // Update children recursively update(2*node a (a + b)/2 x diff) update(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b x diff) // Update node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[2 * node] + segmentTree[2 * node + 1]
La funció recursiva anterior s'executa O (log (max_elem)) (En aquest cas, max_elem és 10^6) i s'utilitza tant per a la inserció com per a la supressió amb les trucades següents:
Ara la funció per trobar l’índex amb KTH “1” on “K” en aquest cas sempre serà (n + 1) / 2 Això funcionarà molt com la cerca binària, podeu pensar -ho com una funció de cerca binària recursiva en un arbre de segments.
Prenem un exemple per entendre que el nostre conjunt té actualment elements {1 4 7 8 9} i, per tant, es representa amb el següent arbre del segment.
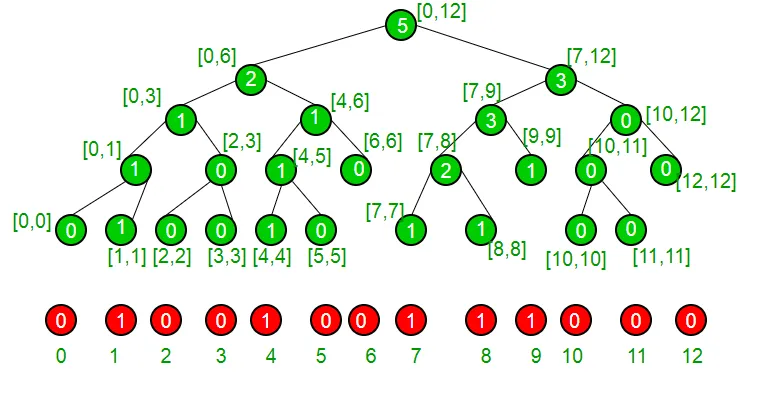
Si estem en un node que no sigui de fulla, estem segurs que té els dos fills, veiem si el nen esquerre té un nombre més o igual de un com a "K" Si és així, estem segurs que el nostre índex es troba a la subtrata esquerra, si no, si la subtera esquerra té menys un nombre d'1 que K, estem segurs que el nostre índex es troba a la subtret dreta. Ho fem recursivament per arribar al nostre índex i a partir d’aquí el tornem.
Algorisme
1.findKth(node a b k) 2. If a != b 3. If segmentTree[ 2 * node ] >= k 4. return findKth(2*node a (a + b)/2 k) 5. else 6. return findKth(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[ 2 * node ]) 7. else 8. return a
La funció recursiva anterior s'executa O (log (max_elem)) .
// A C++ program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree #include
// A Java program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree import java.io.*; class GFG{ public static int maxn = 3000005; public static int max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int[] segmentTree = new int[maxn]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update(int node int a int b int x int diff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth(int node int a int b int k) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return (segmentTree[node] != 0) ? a : -1; } // Insert x in the set public static void insert(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median() { int k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); System.out.println('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()); insert(8); insert(9); System.out.println('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()); delete(1); delete(8); System.out.println('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()); } } // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
# A Python3 program to implement insert delete and # median queries using segment tree maxn = 3000005 max_elem = 1000000 # A global array to store segment tree. # Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. segmentTree = [0 for i in range(maxn)] # Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. # Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and # 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored # in current node. # 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. def update(node a b x diff): global segmentTree # If current node is a leaf node if (a == b and a == x ): # add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff return # If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its # range if (x >= a and x <= b): # update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b)//2 x diff) update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b)//2 + 1 b x diff) # Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1] # Returns k'th node in segment tree def findKth(node a b k): global segmentTree # non-leaf node will definitely have both # children left and right if (a != b): # If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k): return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b)//2 k) # If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b)//2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]) # if at a leaf node return the index it stores # information about return a if (segmentTree[node]) else -1 # insert x in the set def insert(x): update(1 0 max_elem x 1) # delete x from the set def delete(x): update(1 0 max_elem x -1) # returns median element of the set with odd # cardinality only def median(): k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) // 2 return findKth(1 0 max_elem k) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': insert(1) insert(4) insert(7) print('Median for the set {147} ='median()) insert(8) insert(9) print('Median for the set {14789} ='median()) delete(1) delete(8) print('Median for the set {479} ='median()) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
// A C# program to implement insert delete // and median queries using segment tree using System; class GFG{ public static int maxn = 3000005; public static int max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int[] segmentTree = new int[maxn]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update(int node int a int b int x int diff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth(int node int a int b int k) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it // stores information about if (segmentTree[node] != 0) { return a; } else { return -1; } } // Insert x in the set public static void insert(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median() { int k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code static public void Main() { insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()); insert(8); insert(9); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()); delete(1); delete(8); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()); } } // This code is contributed by rag2127
<script> // A Javascript program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree let maxn = 3000005; let max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. let segmentTree = new Array(maxn); for(let i=0;i<maxn;i++) { segmentTree[i]=0; } // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. function update(nodeabxdiff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a Math.floor((a + b) / 2) x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 Math.floor((a + b) / 2) + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree function findKth(nodeabk) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a Math.floor((a + b) / 2) k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 Math.floor((a + b) / 2) + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return (segmentTree[node] != 0) ? a : -1; } // Insert x in the set function insert(x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set function delet(x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only function median() { let k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); document.write('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()+'
'); insert(8); insert(9); document.write('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()+'
'); delet(1); delet(8); document.write('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()+'
'); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 </script>
Sortida:
Median for the set {147} = 4 Median for the set {14789} = 7 Median for the set {479} = 7
Conclusió:
Les tres consultes s’aconsegueixen O (log (max_elem)) En aquest cas, max_elem = 10^6 SO log (max_elem) és aproximadament igual a 20.
L’arbre del segment utilitza O (max_elem) espai.
Si la consulta d’eliminació no hi fos, el problema també s’hauria pogut fer amb un famós algorisme aquí .
