Donat un paper rectangular de dimensions a x b . La tasca consisteix a tallar tot el paper mínim nombre de quadrat peces. Podem triar peces quadrades de qualsevol mida però s'han de tallar sense sobreposar-se ni deixar cap espai addicional .
Exemples:
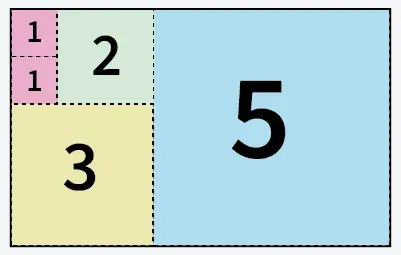
Entrada: a = 5 b = 8
5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 5 X 8
Sortida: 5
Explicació: Podem tallar el paper en 5 quadrats: 1 quadrat de mida 5x5 1 quadrat de mida 3x3 1 quadrat de mida 2x2 i 2 quadrats de mida 1x1.Entrada: a = 13 b = 11
6 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 13 X 11
Sortida: 6
Explicació: Podem tallar el paper en 6 quadrats: 1 quadrat de mida 7x7 1 quadrat de mida 6x6 1 quadrat de mida 5x5 2 quadrats de mida 4x4 i 1 quadrat de mida 1x1.Entrada: a = 6 b = 7
5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 6 X 7
Sortida: 5
Explicació: Podem tallar el paper en 5 quadrats: 1 quadrat de mida 4x4 2 quadrats de mida 3x3 i 2 quadrats de mida 3x3.
Taula de continguts
programa python per a la cerca binària
- [Enfocament incorrecte 1] Ús de la tècnica Greedy
- [Enfocament incorrecte 2] Ús de la programació dinàmica
- [Enfocament correcte] Ús de DFS i programació dinàmica
[Enfocament incorrecte 1] Ús de la tècnica Greedy
A primera vista, pot semblar que el problema es pot resoldre fàcilment tallant primer el quadrat més gran possible del paper, seguit de tallant el quadrat més gran del paper restant i així successivament fins que hem tallat tot el paper. Però aquesta solució és incorrecta.
Per què Greedy Approach no funcionarà?
Considereu un paper de mida 6x7 aleshores si intentem tallar el paper amb ganes ho aconseguirem 7 quadrats: 1 quadrat de mida 6x6 i 6 quadrats de mida 1x1 mentre que la solució correcta és: 5. Per tant, l'enfocament cobdiciós no funcionarà.
[Enfocament incorrecte 2] Ús de la programació dinàmica
Programació dinàmica amb talls verticals o horitzontals: Una altra solució que pot semblar correcta és utilitzar Programació dinàmica . Podem mantenir una taula dp[][] tal que dp[i][j] = nombre mínim de quadrats que es poden tallar del paper de mida i x j . Després per paper de mida axb
c programa per a la comparació de cadenes
- Podem intentar tallar-lo al llarg de cada fila: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) on k pot estar en el rang [1 i - 1].
- Podem intentar tallar-lo al llarg de cada columna: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) on k pot estar en el rang [1 j - 1].
Finalment, el mínim de tots els talls serà la resposta. Però aquesta solució també és incorrecta.
Per què tallar verticalment o horitzontalment amb l'enfocament de programació dinàmica no funcionarà?
Això no funcionarà perquè suposem que un tall vertical o horitzontal sempre dividirà el rectangle en dues parts. Considereu un paper de mida 13x11 aleshores, si intentem tallar el paper utilitzant l'enfocament DP, obtindrem 8 quadrats, però la resposta correcta (com es mostra als exemples) és 6. Per tant, la programació dinàmica no funcionarà.
[Enfocament correcte] Ús de DFS i programació dinàmica
C++El idea és tallar tot el paper utilitzant DFS en de baix a dalt manera. A cada pas, cerqueu la cantonada inferior esquerra del paper i proveu de tallar quadrats de totes les mides possibles des d'aquesta cantonada. Després de tallar un quadrat, torneu a trobar la cantonada inferior esquerra del paper restant per tallar quadrats de totes les mides possibles i així successivament. Però si provem tots els talls possibles des de la cantonada inferior esquerra de totes les mides de paper possibles, seria bastant ineficient. Podem optimitzar-lo utilitzant Programació dinàmica per emmagatzemar els talls mínims per a cada mida de paper possible.
Per identificar de manera única qualsevol mida de paper, podem mantenir una matriu remSq[] de manera que remSq[i] emmagatzemi el nombre de quadrats restants de mida 1x1 a la i-esima columna del paper. Així, per a un paper de mida 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. També per trobar la cantonada inferior esquerra trobarem el primer índex amb el màxim de quadrats restants. Per tant, podem triturar el valor de remSq[] array per trobar una clau única per a tots els valors possibles de remSq[] array.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Sortida
6
Complexitat temporal: O(a^b) per a cadascuna de b columnes podem tenir un quadrat.
Espai auxiliar: O(a^b) a causa de la memorització que emmagatzema cada estat únic.

 5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 5 X 8
5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 5 X 8 6 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 13 X 11
6 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 13 X 11 5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 6 X 7
5 quadrats tallats de Paper de mida 6 X 7