Arbre AVL:
L'arbre AVL és un arbre de cerca binari d'autoequilibri ( BST ) on la diferència entre les altures dels subarbres esquerre i dret no pot ser superior a un per a tots els nodes.
Exemple d'arbre AVL:
L'arbre anterior és AVL perquè les diferències entre les altures dels subarbres esquerre i dret de cada node són menors o iguals a 1.
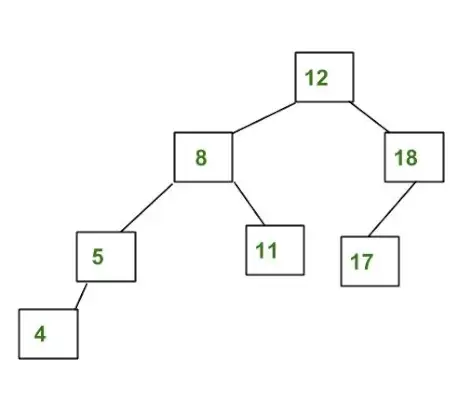
Exemple d'un arbre que NO és un arbre AVL:

L'arbre anterior no és AVL perquè les diferències entre les altures dels subarbres esquerre i dret per a 8 i 12 són més grans que 1.
Per què AVL Trees?
La majoria de les operacions de BST (p. ex., cerca, màx., mínim, inserir, suprimir, etc.) O(h) temps on h és l'alçada del BST. El cost d'aquestes operacions pot arribar a ser O(n) per a Arbre binari esbiaixat . Si ens assegurem que es manté l'alçada de l'arbre O(log(n)) després de cada inserció i supressió, podem garantir un límit superior de O(log(n)) per a totes aquestes operacions. L'alçada d'un arbre AVL és sempre O(log(n)) on n és el nombre de nodes de l'arbre.
Inserció a l'arbre AVL:
Per assegurar-nos que l'arbre donat es mantingui AVL després de cada inserció, hem d'augmentar l'operació d'inserció estàndard de BST per fer un cert reequilibri.
A continuació es mostren dues operacions bàsiques que es poden realitzar per equilibrar un BST sense violar la propietat BST (tecles (esquerra)
- Rotació a l'esquerra
- Rotació dreta
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 i / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Pràctica recomanada Inserció d'arbres AVL Prova-ho!
Passos a seguir per a la inserció:
Sigui el nou node inserit En
- Realitzar estàndard BST inserir per En .
- Començant des de En , viatja amunt i troba el primer node desequilibrat . Deixar Amb ser el primer node desequilibrat, i ser el nen de Amb que ve en el camí de En a Amb i x ser el nét de Amb que ve en el camí de En a Amb .
- Torneu a equilibrar l'arbre fent les rotacions adequades al subarbre amb el qual arrela Amb. Hi pot haver 4 casos possibles que s'han de tractar com x, y i Amb es pot organitzar de 4 maneres.
- A continuació es mostren els 4 arranjaments possibles:
- y és el fill esquerre de z i x és el fill esquerre de y (cas esquerra esquerra)
- y és el fill esquerre de z i x és el fill dret de y (cas esquerre dret)
- y és el fill dret de z i x és el fill dret de y (cas de la dreta)
- y és el fill dret de z i x és el fill esquerre de y (cas esquerra dreta)
A continuació es mostren les operacions a realitzar en els 4 casos esmentats anteriorment. En tots els casos, només ens cal reequilibrar el subarbre arrelat amb Amb i l'arbre complet s'equilibra a mesura que l'alçada del subarbre (després de les rotacions adequades) arrela amb Amb torna a ser el mateix que abans de la inserció.
1. Esquerra Esquerra majúscula
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Esquerra Dreta Cas
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Dreta Dreta Cas
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Dreta Esquerra Cas
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Il·lustració de la inserció a l'arbre AVL





Enfocament:
La idea és utilitzar la inserció BST recursiva, després de la inserció, obtenim punters a tots els avantpassats un per un de manera ascendente. Per tant, no necessitem un punter principal per pujar. El codi recursiu en si mateix viatja cap amunt i visita tots els avantpassats del nou node inserit.
Seguiu els passos esmentats a continuació per implementar la idea:
- Fes el normal Inserció de BST.
- El node actual ha de ser un dels avantpassats del nou node inserit. Actualitza el alçada del node actual.
- Obteniu el factor d'equilibri (alçada del subarbre esquerre - alçada del subarbre dret) del node actual.
- Si el factor d'equilibri és superior a 1, aleshores el node actual està desequilibrat i estem o bé al Esquerra Esquerre cas o esquerra Cas dret . Per comprovar si ho és cas esquerre esquerre o no, compareu la clau que s'acaba d'inserir amb la clau del fitxer arrel del subarbre esquerre .
- Si el factor d'equilibri és inferior a -1 , aleshores el node actual està desequilibrat i estem en el cas Dreta Dreta o Dreta-Esquerra. Per comprovar si és o no el cas del dret dret, compareu la clau que s'acaba d'inserir amb la clau de l'arrel del subarbre dret.
A continuació es mostra la implementació de l'enfocament anterior:
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->alçada;>>> // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>>> /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->clau = clau;>>> // added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->esquerra;>>> // Perform rotation> >x->dreta = y;>>> // Update heights> >y->alçada = màxima (alçada (y->esquerra),> >height(y->dreta)) + 1;>>> >height(x->dreta)) + 1;>>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->dret;>>> // Perform rotation> >y->esquerra = x;>>> // Update heights> >x->alçada = màxima (alçada (x->esquerra),> >height(x->dreta)) + 1;>>> >height(y->dreta)) + 1;>>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->esquerra) - alçada (N->dreta);>>> // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->esquerra = inserir (node->esquerra, clau);>>> if> (key>node->clau)>>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->alçada = 1 + màxim (alçada (node->esquerra),> >height(node->dret));>>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && tecla esquerra->tecla)>>> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->dreta->tecla)>>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && clau> node->esquerra->tecla)> >{> >node->esquerra = leftRotate(node->esquerra);>>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->clau)>>> >node->dreta = dretaRotar(node->dreta);>>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->esquerra); preordre (arrel->dreta); } } // Codi del controlador int main() { Node *root = NULL; /* Construcció de l'arbre donat a la figura anterior */ root = insert(root, 10); arrel = inserir (arrel, 20); arrel = inserir (arrel, 30); arrel = inserir (arrel, 40); arrel = inserir (arrel, 50); arrel = inserir (arrel, 25); /* L'arbre AVL construït seria 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->alçada;>>> // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>>> /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->clau = clau;>>> return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->esquerra;>>> Node *T2 = x->dret;>>> // Perform rotation> >x->dreta = y;>>> // Update heights> >y->alçada = màxima (alçada (y->esquerra),> >height(y->dreta)) + 1;>>> >height(x->dreta)) + 1;>>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->dret;>>> Node *T2 = y->esquerra;>>> // Perform rotation> >y->esquerra = x;>>> // Update heights> >x->alçada = màxima (alçada (x->esquerra),> >height(x->dreta)) + 1;>>> >height(y->dreta)) + 1;>>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->esquerra) - alçada (N->dreta);>>> // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->esquerra = inserir (node->esquerra, clau);>>> if> (key>node->clau)>>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->alçada = 1 + màxim (alçada (node->esquerra),> >height(node->dret));>>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && tecla esquerra->tecla)>>> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->dreta->tecla)>>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && clau> node->esquerra->tecla)> >{> >node->esquerra = leftRotate(node->esquerra);>>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->clau)>>> >node->dreta = dretaRotar(node->dreta);>>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->clau);>>> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>>> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = inserir (node.right, clau); else // Les claus duplicades no es permeten retornar el node; /* 2. Actualitza l'alçada d'aquest node avantpassat */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Obteniu el factor d'equilibri d'aquest node avantpassat per comprovar si aquest node es va desequilibrar */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Si aquest node es desequilibra, llavors // hi ha 4 casos Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (equilibri)<-1 && key>node.right.key) retorna leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (equilibri> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); tornar a la dretaGirar (node); } // Dreta Esquerra Cas si (equilibri<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python 3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 i la clau retornen self.rightRotate(arrel) # Cas 2 - Dreta Dret si s'equilibra<-1 and key>root.right.val: retorna self.leftRotate (arrel) # Cas 3 - Esquerra Dreta si equilibri> 1 i clau> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate (arrel.esquerra) retorna self.rightRotate (arrel ) # Cas 4 - Dreta Esquerra si s'equilibra<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = inserir (node.right, clau); else // Les claus duplicades no es permeten retornar el node; /* 2. Actualitza l'alçada d'aquest node avantpassat */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Obteniu el factor d'equilibri d'aquest node avantpassat per comprovar si aquest node es va desequilibrar */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Si aquest node es desequilibra, llavors // hi ha 4 casos Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // Left Right Rotate if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.left = leftRotate(node.left) // Right Left Rotate si (equilibri).<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b? a: b;>>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = this.insert (node.right, clau); // No es permeten les claus duplicades, sinó retornen el node; /* 2. Actualitza l'alçada d'aquest node avantpassat */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(node.left), this.height(node.right)); /* 3. Obteniu el factor d'equilibri d'aquest node avantpassat per comprovar si aquest node es va desequilibrar */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Si aquest node es desequilibra, // hi ha 4 casos Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) retorna això. leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = this.leftRotate (node.rightRotate } // Right); Left Case if (equilibri<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root); > |
>
>Sortida
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Anàlisi de complexitat
Complexitat temporal: O(log(n)), per a la inserció
Espai auxiliar: O(1)
javascript més proper
Les operacions de rotació (gir a l'esquerra i a la dreta) triguen un temps constant, ja que només s'hi canvien alguns punters. Actualitzar l'alçada i obtenir el factor d'equilibri també requereix temps constant. Així, la complexitat temporal de la inserció AVL segueix sent la mateixa que la inserció BST, que és O(h) on h és l'alçada de l'arbre. Com que l'arbre AVL està equilibrat, l'alçada és O (Logn). Així, la complexitat temporal de la inserció AVL és O (Logn).
Comparació amb Red Black Tree:
L'arbre AVL i altres arbres de cerca d'autoequilibri com Red Black són útils per fer totes les operacions bàsiques en temps O(log n). Els arbres AVL són més equilibrats en comparació amb els arbres vermell-negre, però poden provocar més rotacions durant la inserció i la supressió. Per tant, si la vostra aplicació implica moltes insercions i supressions freqüents, hauríeu de preferir els arbres vermells negres. I si les insercions i les supressions són menys freqüents i la cerca és l'operació més freqüent, s'hauria de preferir l'arbre AVL sobre Red Black Tree .
A continuació es mostra la publicació per eliminar-la a l'arbre AVL:
Arbre AVL | Set 2 (supressió)
