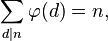La funció Totient d'Euler Φ(n) per a una entrada n és el recompte de nombres de {1, 2, 3, …, n-1} que són relativament primers a n, és a dir, els nombres el MCD (Màxim Comú Divisor) dels quals amb n és 1.
Exemples :
Φ(1) = 1
mcd(1, 1) és 1
Φ(2) = 1
mcd(1, 2) és 1, però mcd(2, 2) és 2.
Φ(3) = 2
mcd(1, 3) és 1 i mcd(2, 3) és 1
Φ(4) = 2
mcd(1, 4) és 1 i mcd(3, 4) és 1
Φ(5) = 4
mcd(1, 5) és 1, mcd(2, 5) és 1,
mcd(3, 5) és 1 i mcd(4, 5) és 1
Φ(6) = 2
mcd(1, 6) és 1 i mcd(5, 6) és 1,
Pràctica recomanada Funció Euler Totient Prova-ho!
Com calcular Φ (n) per a una entrada n?
A solució senzilla és iterar per tots els nombres de l'1 a n-1 i comptar els nombres amb mcd amb n com a 1. A continuació es mostra la implementació del mètode senzill per calcular la funció Totient d'Euler per a un enter d'entrada n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python 3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Sortida
phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
El codi anterior crida a la funció gcd O(n) vegades. La complexitat temporal de la funció mcd és O(h) on h és el nombre de dígits en un nombre més petit de dos nombres donats. Per tant, un límit superior al complexitat temporal de la solució anterior és O(N^2 log N) [Com Φ pot haver-hi com a màxim Log10n dígits en tots els nombres de l'1 al n]
Espai auxiliar: O (log N)
A continuació hi ha a Millor Solució . La idea es basa en la fórmula del producte d'Euler que estableix que el valor de les funcions totient està per sota del producte dels factors primers globals p de n.
La fórmula diu bàsicament que el valor de Φ(n) és igual al subproducte multiplicat per n de (1 – 1/p) per a tots els factors primers p de n. Per exemple, el valor de Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Podem trobar tots els factors primers utilitzant la idea utilitzada a això publicació.
1) Inicialitzar: resultat = n
2) Executeu un bucle de 'p' = 2 a sqrt(n), feu el següent per a cada 'p'.
a) Si p divideix n, aleshores
Conjunt: resultat = resultat * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Dividiu totes les ocurrències de p en n.
3) Torna el resultat
A continuació es mostra la implementació de la fórmula del producte d'Euler.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer retorna (int)resultat; } // Codi del controlador int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer retorna (int)resultat; } // Programa controlador per provar la funció anterior int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer retorna (int)resultat; } // Programa de controlador per provar la funció anterior public static void main(String args[]) { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python 3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : resultat -= resultat // n #Com que al conjunt {1,2,...,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n #si n és un nombre primer return int(resultat) # Controlador programa per provar la funció anterior per a n en el rang (1, 11): print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Aquest codi és aportat per Nikita Tiwari.>>>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer retorna (int)resultat; } // Codi del controlador public static void Main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer retorna parseInt(resultat); } // Codi del controlador per a (deixar n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $resultat -= $resultat / $n; //Com que en el conjunt {1,2,....,n-1}, tots els nombres són relativament primers amb n //si n és un nombre primer return intval($resultat); } // Codi del controlador per a ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>
Sortida Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Complexitat temporal: O(Φ n log n)
Espai auxiliar: O(1)
Podem evitar els càlculs de coma flotant amb el mètode anterior. La idea és comptar tots els factors primers i els seus múltiples i restar aquest recompte de n per obtenir el valor de la funció totient (els factors primers i els múltiples de factors primers no tindran mcd com a 1)
1) Inicialitzar el resultat com n
2) Considereu cada nombre 'p' (on 'p' varia de 2 a Φ(n)).
Si p divideix n, feu el següent
a) Resteu tots els múltiples de p d'1 a n [tots els múltiples de p
tindrà mcd més d'1 (almenys p) amb n]
b) Actualitzeu n dividint-lo repetidament per p.
3) Si la n reduïda és superior a 1, elimineu tots els múltiples
de n a partir del resultat.
A continuació es mostra la implementació de l'algorisme anterior.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; retornar el resultat; } // Codi del controlador int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; retornar el resultat; } // Programa controlador per provar la funció anterior int main() { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; retornar el resultat; } // Codi del controlador public static void main (String[] args) { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python 3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): resultat -= int(resultat / n); retornar el resultat; # Codi del controlador per a n en el rang (1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Aquest codi és aportat # per mits>>>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat / n; retornar el resultat; } // Codi del controlador static public void Main () { int n; per (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= parseInt(resultat / n); retornar el resultat; } // Codi del controlador per a (deixar n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $resultat -= (int)$resultat / $n; retornar $resultat; } // Codi del controlador per a ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>>
Sortida Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Complexitat temporal: O(Φ n log n)
Espai auxiliar: O(1)
Prenguem un exemple per entendre l'algorisme anterior.
n = 10.
Inicialitzar: resultat = 10
2 és un factor primer, per tant n = n/i = 5, resultat = 5
3 no és un factor primer.
El bucle for s'atura després de 3, ja que 4*4 no és menor o igual
a 10.
Després del bucle for, resultat = 5, n = 5
Com que n> 1, resultat = resultat - resultat/n = 4
Algunes propietats interessants de la funció Totient d'Euler
1) Per a nombre primer p ,phi(p) = p – 1
Prova:
on k és qualsevol nombre aleatori ik
eq p gcd(p, k) = 1 és1 , és a dir, el nombre p mateix, per tant, restant 1 de pphi(p) = p - 1
Exemples :
phi(5) = 5 - 1 = 4 phi(13) = 13 - 1 = 12 phi(29) = 29 - 1 = 28
2) Per dos nombres primers a i b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) = (a – 1) cdot (b – 1) , utilitzat en Algoritme RSA
Prova:
phi(acdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) , on a i b són nombres primersphi(a) = a - 1 ,phi(b) = b - 1 frac{a cdot b} {a} =b Múltiples totals de b de 1 a ab =frac{a cdot b} {b} =a Exemple: a = 5, b = 7, ab = 35Múltiples de a =frac {35} {5} = 7 {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35}Múltiples de b =frac {35} {7} = 5 {7, 14, 21, 28, 35}ab dues vegades en múltiples de a i múltiples de b, per tant, Múltiples totals = a + b - 1 (amb la qual cosagcd
eq 1 ambab )phi(ab) = ab - (a + b - 1) , eliminant tots els números ambgcd
eq 1 ambab phi(ab) = a(b - 1) - (b - 1) phi(ab) = (a - 1) cdot (b - 1) phi(ab) = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Exemples :
phi(5 cdot 7) = phi(5) cdot phi(7) = (5 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 24 phi(3 cdot 5) = phi(3) cdot phi(5) = (3 - 1) cdot (5 - 1) = 8 phi(3 cdot 7) = phi(3) cdot phi(7) = (3 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 12
3) Per un nombre primer p ,phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k – p ^ {k – 1}
Prova:
phi(p^k) = p ^ k - p ^{k - 1} , on p és un nombre primerp ^ k = p ^ k Múltiples totals dep = frac {p ^ k} {p} = p ^ {k - 1} Eliminant aquests múltiples com amb ellsgcd
eq 1 p ^ k = 32Múltiples de 2 (com amb ellsgcd
eq 1 ) = 32 / 2 = 16 {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32}phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k - p ^ {k - 1}
Exemples :
phi(2 ^ 5) = 2 ^ 5 - 2 ^ {5 - 1} = 32 - 16 = 16 phi(5 ^ 3) = 5 ^ 3 - 5 ^ {3 - 1} = 125 - 25 = 100 phi(3 ^ 5) = 3 ^ 5 - 3 ^ {5 - 1} = 243 - 81 = 162
4) Per dos números a i b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))}
Cas especial: mcd(a, b) = 1
phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {1} {phi(1)} = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Exemples :
Cas especial : gcd(a, b) = 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) phi(2 cdot 9) = phi(2) cdot phi(9) = 1 cdot 6 = 6 phi(8 cdot 9) = phi(8) cdot phi(9) = 4 cdot 6 = 24 phi(5 cdot 6) = phi(5) cdot phi(6) = 4 cdot 2 = 8 gcd(a, b)
eq 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))} phi(4 cdot 6) = phi(4) cdot phi(6) cdot frac {gcd(4, 6)} {phi(gcd(4, 6))} = 2 cdot 2 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 2 cdot 2 = 8 phi(4 cdot 8) = phi(4) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(4, 8)} {phi(gcd(4, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{4}{2} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16 phi(6 cdot 8) = phi(6) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(6, 8)} {phi(gcd(6, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16
5) La suma de valors de les funcions totient de tots els divisors de n és igual a n.
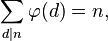
Exemples :
n = 6
factors = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(3) + phi(6) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 6phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(4) + phi(8) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 8phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(5) + phi(10) = 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 10
6) La característica més famosa i important s'expressa en Teorema d'Euler :
El teorema diu que si n i a són copprims
Aleshores, nombres enters positius (o primers relativament primers).
aΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
El Criptosistema RSA es basa en aquest teorema:
En el cas particular quan m és primer diem p, el teorema d'Euler es converteix en l'anomenat El petit teorema de Fermat :
ap-1Φ 1 (contra p)
7) El nombre de generadors d'un grup cíclic finit sota l'addició mòdul n és Φ(n) .
Article relacionat:
Funció Totient d'Euler per a tots els nombres menors o iguals a n
Funció Euler Totient optimitzada per a avaluacions múltiples
com revelar aplicacions ocultes
Referències:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/