En C++, l'herència és un procés en el qual un objecte adquireix totes les propietats i comportaments del seu objecte pare automàticament. D'aquesta manera, podeu reutilitzar, ampliar o modificar els atributs i comportaments que es defineixen en una altra classe.
En C++, la classe que hereta els membres d'una altra classe s'anomena classe derivada i la classe els membres de la qual s'hereten s'anomena classe base. La classe derivada és la classe especialitzada per a la classe base.
Avantatge de l'herència C++
Reutilitzabilitat del codi: Ara podeu reutilitzar els membres de la vostra classe de pares. Per tant, no cal tornar a definir el membre. Per tant, es requereix menys codi a la classe.
memòria de registre
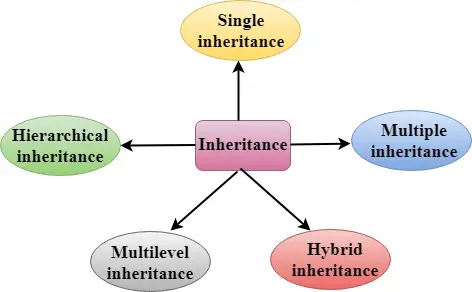
Tipus d'Herència
C++ admet cinc tipus d'herència:
- Herència única
- Herència múltiple
- Herència jeràrquica
- Herència multinivell
- Herència híbrida
Classes derivades
Una classe derivada es defineix com la classe derivada de la classe base.
com revelar aplicacions ocultes
La sintaxi de la classe derivada:
|_+_|En el cas anterior, la funció de la classe derivada anul·la el mètode de la classe base. Per tant, cridar a la funció display() simplement cridarà a la funció definida a la classe derivada. Si volem invocar la funció de classe base, podem utilitzar l'operador de resolució de classes.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } Herència híbrida C++
L'herència híbrida és una combinació de més d'un tipus d'herència.

Vegem un exemple senzill:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> Herència jeràrquica C++
L'herència jeràrquica es defineix com el procés de derivar més d'una classe d'una classe base.

Sintaxi de l'herència jeràrquica:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } Vegem un exemple senzill:
herència en c++
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>