Gestors de disseny de Java
Els LayoutManagers s'utilitzen per organitzar components d'una manera particular. El Gestors de disseny de Java ens facilita controlar el posicionament i la mida dels components en formularis GUI. LayoutManager és una interfície implementada per totes les classes de gestors de maquetació. Hi ha les classes següents que representen els gestors de maquetació:
1 milió en dígits
- java.awt.BorderLayout
- java.awt.FlowLayout
- java.awt.GridLayout
- java.awt.CardLayout
- java.awt.GridBagLayout
- javax.swing.BoxLayout
- javax.swing.GroupLayout
- javax.swing.ScrollPaneLayout
- javax.swing.SpringLayout, etc.
Java BorderLayout
El BorderLayout s'utilitza per organitzar els components en cinc regions: nord, sud, est, oest i centre. Cada regió (àrea) només pot contenir un component. És la disposició per defecte d'un marc o finestra. El BorderLayout proporciona cinc constants per a cada regió:
Constructors de la classe BorderLayout:
Exemple de classe BorderLayout: utilitzant el constructor BorderLayout().
Nom de l'arxiu: Border.java
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Border { JFrame f; Border() { f = new JFrame(); // creating buttons JButton b1 = new JButton('NORTH');; // the button will be labeled as NORTH JButton b2 = new JButton('SOUTH');; // the button will be labeled as SOUTH JButton b3 = new JButton('EAST');; // the button will be labeled as EAST JButton b4 = new JButton('WEST');; // the button will be labeled as WEST JButton b5 = new JButton('CENTER');; // the button will be labeled as CENTER f.add(b1, BorderLayout.NORTH); // b1 will be placed in the North Direction f.add(b2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); // b2 will be placed in the South Direction f.add(b3, BorderLayout.EAST); // b2 will be placed in the East Direction f.add(b4, BorderLayout.WEST); // b2 will be placed in the West Direction f.add(b5, BorderLayout.CENTER); // b2 will be placed in the Center f.setSize(300, 300); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Border(); } } Sortida:
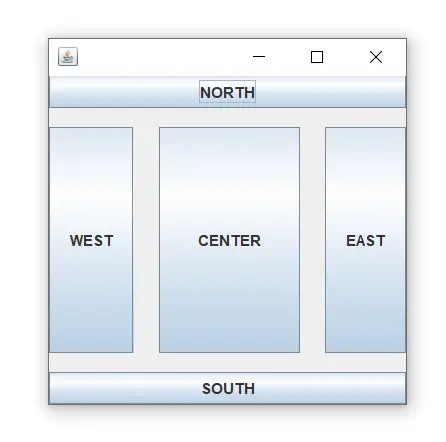 descarregueu aquest exemple
descarregueu aquest exempleExemple de classe BorderLayout: utilitzant el constructor BorderLayout(int hgap, int vgap)
L'exemple següent insereix espais horitzontals i verticals entre botons mitjançant el constructor parametritzat BorderLayout(int hgap, int gap)
Nom de l'arxiu: BorderLayoutExample.java
// import statement import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BorderLayoutExample { JFrame jframe; // constructor BorderLayoutExample() { // creating a Frame jframe = new JFrame(); // create buttons JButton btn1 = new JButton('NORTH'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('SOUTH'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('EAST'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('WEST'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('CENTER'); // creating an object of the BorderLayout class using // the parameterized constructor where the horizontal gap is 20 // and vertical gap is 15. The gap will be evident when buttons are placed // in the frame jframe.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20, 15)); jframe.add(btn1, BorderLayout.NORTH); jframe.add(btn2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); jframe.add(btn3, BorderLayout.EAST); jframe.add(btn4, BorderLayout.WEST); jframe.add(btn5, BorderLayout.CENTER); jframe.setSize(300,300); jframe.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new BorderLayoutExample(); } } Sortida:

Java BorderLayout: sense especificar la regió
El mètode add() de la classe JFrame pot funcionar fins i tot quan no especifiquem la regió. En aquest cas, només es mostra el darrer component afegit al marc i tots els components afegits anteriorment es descarten. L'últim component cobreix tota l'àrea. L'exemple següent mostra el mateix.
Nom de l'arxiu: BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample.java
// import statements import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample { JFrame jframe; // constructor BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample() { jframe = new JFrame(); JButton btn1 = new JButton('NORTH'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('SOUTH'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('EAST'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('WEST'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('CENTER'); // horizontal gap is 7, and the vertical gap is 7 // Since region is not specified, the gaps are of no use jframe.setLayout(new BorderLayout(7, 7)); // each button covers the whole area // however, the btn5 is the latest button // that is added to the frame; therefore, btn5 // is shown jframe.add(btn1); jframe.add(btn2); jframe.add(btn3); jframe.add(btn4); jframe.add(btn5); jframe.setSize(300,300); jframe.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample(); } } Sortida:

