std::shared_ptr és un dels punters intel·ligents introduïts a C++11. A diferència d'un simple punter, té un bloc de control associat que fa un seguiment del recompte de referència per a l'objecte gestionat. Aquest recompte de referències es comparteix entre totes les còpies de les instàncies shared_ptr que apunten al mateix objecte, garantint una gestió i supressió de la memòria adequada.
Requisits previs: Apuntadors en C++ , Punters intel·ligents en C++ .
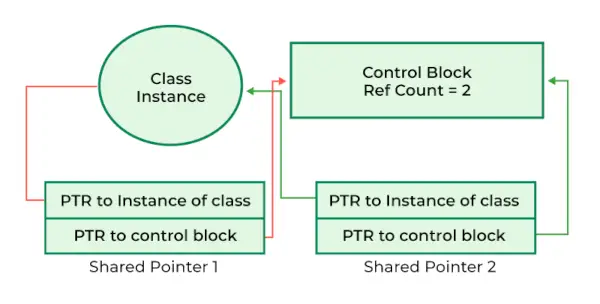
Punter compartit en C++
Sintaxi de std::shared_ptr
El shared_ptr de tipus T es pot declarar com:
std::shared_ptr ptr_name;>
Inicialització dels objectes shared_ptr
Podem inicialitzar shared_ptr mitjançant els mètodes següents:
1. Inicialització mitjançant un punter nou
shared_ptr ptr (new T()); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared (new T());>
2. Inicialització utilitzant el punter existent
shared_ptr ptr(already_existing_pointer); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared(already_existing_pointer);>
Mètodes de membres de shared_ptr
A continuació es mostren alguns membres associats a shared_ptr:
| Mètode | Descripció |
|---|---|
| restablir () | Restableix el std::shared_ptr a buit, alliberant la propietat de l'objecte gestionat. |
| use_count() | Retorna el recompte de referència actual, que indica quantes instàncies std::shared_ptr comparteixen la propietat. |
| únic () | Comproveu si només hi ha un std::shared_ptr propietari de l'objecte (el nombre de referències és 1). |
| aconseguir() | Retorna un punter en brut a l'objecte gestionat. Aneu amb compte quan utilitzeu aquest mètode. |
| intercanvi (shr_ptr2) | intercanvia el contingut (propietat) de dues instàncies std::shared_ptr. |
Exemples de std::shared_ptr
Exemple 1:
C++
>
>Sortida
0x1365c20 A::show() A::show() 0x1365c20 0x1365c20 2 2 0 1 0x1365c20>
Exemple 2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of make_shared> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >// Creating shared pointers using std::make_shared> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr1 = make_shared<>int>>(42);> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr2 = make_shared<>int>>(24);> >// Accessing the values using the dereference operator> >// (*)> >cout << 'Value 1: ' << *shr_ptr1 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 2: ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >// Using the assignment operator (=) to share ownership> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr3 = shr_ptr1;> >// Checking if shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3> >// point to the same object> >if> (shr_ptr1 == shr_ptr3) {> >cout << 'shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 '> >'point to the same object.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Swapping the contents of shared pointer 2 and shared> >// pointer 3> >shr_ptr2.swap(shr_ptr3);> >// Checking the values after the swap> >cout << 'Value 2 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 3 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr3 << endl;> >// Using logical operators to check if shared pointers> >// are valid> >if> (shr_ptr1 && shr_ptr2) {> >cout << 'Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer '> >'2 are valid.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Resetting a shared pointer> >shr_ptr1.reset();> }> |
>
>Sortida
Value 1: 42 Value 2: 24 shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 point to the same object. Value 2 (after swap): 42 Value 3 (after swap): 24 Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 2 are valid.>
Exemple 3: Implementació d'una llista enllaçada amb std::shared_ptr
C++
#include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Define a singly linked list node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >shared_ptr next;> >Node(>int> val)> >: data(val)> >, next(NULL)> >{> >}> };> class> LinkedList {> public>:> >LinkedList()> >: head(NULL)> >{> >}> >// Insert a new node at the end of the linked list> >void> insert(>int> val)> >{> >shared_ptr newNode = make_shared(val);> >if> (!head) {> >head = newNode;> >}> >else> {> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->següent) {> >current = current->següent;> >}> >current->següent = nouNode;> >}> >}> >// Delete a node with a given value from the linked list> >void> del(>int> val)> >{> >if> (!head) {> >return>;> >}> >if> (head->dades == val) {> >head = head->següent;> >return>;> >}> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->següent> >&& current->següent->dades != val) {> >current = current->següent;> >}> >if> (current->següent && actual->següent->dades == val) {> >current->següent = actual->següent->següent;> >}> >}> >// Traverse and print the linked list> >void> Print()> >{> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current) {> >cout current = current->Pròxim; } cout<< 'NULL' << endl; } private: shared_ptr head; }; int main() { LinkedList linkedList; // Insert nodes into the linked list linkedList.insert(1); linkedList.insert(2); linkedList.insert(3); // Print the linked list cout << 'Linked List: '; linkedList.Print(); // Delete a node and print the updated linked list linkedList.del(2); cout << 'Linked List after deleting 2: '; linkedList.Print(); return 0; }> |
>
Funció prototip de c++
>Sortida
