Fusiona l'ordenació és un algorisme d'ordenació que segueix el divideix i conquereix enfocament. Funciona dividint recursivament la matriu d'entrada en subarrays més petits i ordenant-los i després fusionant-los de nou per obtenir la matriu ordenada.
Com comprovar els números bloquejats a Android
En termes simples, podem dir que el procés de combinar ordenar és dividir la matriu en dues meitats, ordenar cada meitat i després tornar a fusionar les meitats ordenades. Aquest procés es repeteix fins que s'ordena tota la matriu.
Algoritme d'ordenació combinada
Com funciona Merge Sort?
L'ordenació combinada és un algorisme d'ordenació popular conegut per la seva eficiència i estabilitat. Segueix el divideix i conquereix enfocament per ordenar un conjunt d'elements donat.
Aquí teniu una explicació pas a pas de com funciona l'ordenació de combinació:
- Dividir: Dividiu la llista o la matriu de manera recursiva en dues meitats fins que ja no es pugui dividir.
- Conquerir: Cada subbarray s'ordena individualment mitjançant l'algorisme d'ordenació combinada.
- Fusionar: Els subbarrays ordenats es fusionen de nou en ordre ordenat. El procés continua fins que s'han fusionat tots els elements d'ambdues subbarras.
Il·lustració de Merge Sort:
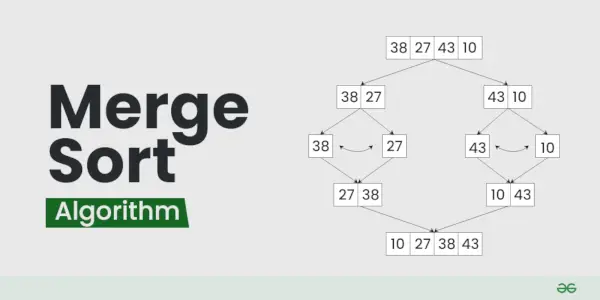
Anem a ordenar la matriu o la llista [38, 27, 43, 10] utilitzant Merge Sort
Pràctica recomanada Prova-ho!Vegem el funcionament de l'exemple anterior:
Dividir:
- [38, 27, 43, 10] es divideix en [38, 27 ] i [43, 10] .
- [38, 27] es divideix en [38] i [27] .
- [43, 10] es divideix en [43] i [10] .
Conquerir:
- [38] ja està ordenat.
- [27] ja està ordenat.
- [43] ja està ordenat.
- [10] ja està ordenat.
Fusionar:
- Fusionar [38] i [27] aconseguir [27, 38] .
- Fusionar [43] i [10] aconseguir [10,43] .
- Fusionar [27, 38] i [10,43] per obtenir la llista ordenada final [10, 27, 38, 43]
Per tant, la llista ordenada és [10, 27, 38, 43] .
ordre per sql aleatori
Implementació de Merge Sort:
C++ // C++ program for Merge Sort #include using namespace std; // Merges two subarrays of array[]. // First subarray is arr[begin..mid] // Second subarray is arr[mid+1..end] void merge(int array[], int const left, int const mid, int const right) { int const subArrayOne = mid - left + 1; int const subArrayTwo = right - mid; // Create temp arrays auto *leftArray = new int[subArrayOne], *rightArray = new int[subArrayTwo]; // Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for (auto i = 0; i < subArrayOne; i++) leftArray[i] = array[left + i]; for (auto j = 0; j < subArrayTwo; j++) rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j]; auto indexOfSubArrayOne = 0, indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0; int indexOfMergedArray = left; // Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne && indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { if (leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; } else { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; } indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // left[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // right[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; indexOfMergedArray++; } delete[] leftArray; delete[] rightArray; } // begin is for left index and end is right index // of the sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int array[], int const begin, int const end) { if (begin>= final) tornar; int mid = començar + (final - començar) / 2; mergeSort (matriu, començar, mig); mergeSort (matriu, mig + 1, final); combinar (matriu, començar, mig, final); } // FUNCIONS D'UTILITAT // Funció per imprimir una matriu void printArray(int A[], int size) { for (int i = 0; i< size; i++) cout << A[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); cout << 'Given array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); cout << '
Sorted array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; } // This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi // This code was revised by Joshua Estes> C // C program for Merge Sort #include #include // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { int i, j, k; int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[n1], R[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r i = 0; j = 0; k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves mergeSort(arr, l, m); mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r); merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // Function to print an array void printArray(int A[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) printf('%d ', A[i]); printf('
'); } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); printf('Given array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); printf('
Sorted array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; }> Java // Java program for Merge Sort import java.io.*; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[] = new int[n1]; int R[] = new int[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indices of first and second subarrays int i = 0, j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to print array of size n static void printArray(int arr[]) { int n = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) System.out.print(arr[i] + ' '); System.out.println(); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; System.out.println('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); System.out.println('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */> Python # Merges two subarrays of array[]. # First subarray is arr[left..mid] # Second subarray is arr[mid+1..right] def merge(array, left, mid, right): subArrayOne = mid - left + 1 subArrayTwo = right - mid # Create temp arrays leftArray = [0] * subArrayOne rightArray = [0] * subArrayTwo # Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for i in range(subArrayOne): leftArray[i] = array[left + i] for j in range(subArrayTwo): rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j] indexOfSubArrayOne = 0 # Initial index of first sub-array indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0 # Initial index of second sub-array indexOfMergedArray = left # Initial index of merged array # Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne and indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: if leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 else: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of left[], if any while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of right[], if any while indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # begin is for left index and end is right index # of the sub-array of arr to be sorted def mergeSort(array, begin, end): if begin>= final: return mid = begin + (end - begin) // 2 mergeSort(array, begin, mid) mergeSort(array, mid + 1, end) merge(array, begin, mid, end) # Funció per imprimir una matriu def printArray(matriu, mida): per i dins l'interval(mida): print(matriu[i], final=' ') print() # Codi del controlador if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [12 , 11, 13, 5, 6, 7] arr_size = len(arr) print('La matriu donada és') printArray(arr, arr_size) mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1) print('
Matriu ordenada és') printArray(arr, arr_size)> C# // C# program for Merge Sort using System; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of []arr. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int[] arr, int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two // subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int[] L = new int[n1]; int[] R = new int[n2]; int i, j; // Copy data to temp arrays for (i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indexes of first // and second subarrays i = 0; j = 0; // Initial index of merged // subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that // sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int[] arr, int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to // print array of size n static void printArray(int[] arr) { int n = arr.Length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Console.Write(arr[i] + ' '); Console.WriteLine(); } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; Console.WriteLine('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1); Console.WriteLine('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } // This code is contributed by Princi Singh> Javascript // JavaScript program for Merge Sort // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(arr, l, m, r) { var n1 = m - l + 1; var n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays var L = new Array(n1); var R = new Array(n2); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (var i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (var j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] // Initial index of first subarray var i = 0; // Initial index of second subarray var j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray var k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // L[], if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // R[], if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is // right index of the sub-array // of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(arr,l, r){ if(l>=r){ retorn; } var m =l+ parseInt((r-l)/2); mergeSort(arr,l,m); mergeSort(arr,m+1,r); fusionar(arr,l,m,r); } // Funció per imprimir una funció de matriu printArray(A, size) { for (var i = 0; i< size; i++) console.log( A[i] + ' '); } var arr = [ 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 ]; var arr_size = arr.length; console.log( 'Given array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); console.log( 'Sorted array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); // This code is contributed by SoumikMondal> PHP /* PHP recursive program for Merge Sort */ // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(&$arr, $l, $m, $r) { $n1 = $m - $l + 1; $n2 = $r - $m; // Create temp arrays $L = array(); $R = array(); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for ($i = 0; $i < $n1; $i++) $L[$i] = $arr[$l + $i]; for ($j = 0; $j < $n2; $j++) $R[$j] = $arr[$m + 1 + $j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] $i = 0; $j = 0; $k = $l; while ($i < $n1 && $j < $n2) { if ($L[$i] <= $R[$j]) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; } else { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; } $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while ($i < $n1) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while ($j < $n2) { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; $k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(&$arr, $l, $r) { if ($l < $r) { $m = $l + (int)(($r - $l) / 2); // Sort first and second halves mergeSort($arr, $l, $m); mergeSort($arr, $m + 1, $r); merge($arr, $l, $m, $r); } } // Function to print an array function printArray($A, $size) { for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++) echo $A[$i].' '; echo '
'; } // Driver code $arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7); $arr_size = sizeof($arr); echo 'Given array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); mergeSort($arr, 0, $arr_size - 1); echo '
Sorted array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); return 0; //This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli ?>> Sortida
Given array is 12 11 13 5 6 7 Sorted array is 5 6 7 11 12 13>
Anàlisi de complexitat de l'ordenació de fusió:
Complexitat temporal:
- Millor cas: O(n log n), quan la matriu ja està ordenada o gairebé ordenada.
- Cas mitjà: O(n log n), quan la matriu està ordenada aleatòriament.
- Pitjor dels casos: O(n log n), quan la matriu s'ordena en ordre invers.
Complexitat espacial: O(n), es necessita espai addicional per a la matriu temporal utilitzada durant la fusió.
Avantatges de Merge Sort:
- Estabilitat : L'ordenació combinada és un algorisme d'ordenació estable, el que significa que manté l'ordre relatiu d'elements iguals a la matriu d'entrada.
- Rendiment garantit en el pitjor dels casos: L'ordenació de combinació té una complexitat temporal en el pitjor dels casos O(N logN) , el que significa que funciona bé fins i tot en grans conjunts de dades.
- Fàcil d'implementar: L'enfocament de dividir i vencer és senzill.
Desavantatge de l'ordenació combinada:
- Complexitat espacial: L'ordenació combinada requereix memòria addicional per emmagatzemar les submatrius combinades durant el procés d'ordenació.
- No al lloc: L'ordenació combinada no és un algorisme d'ordenació in situ, el que significa que requereix memòria addicional per emmagatzemar les dades ordenades. Això pot ser un desavantatge en aplicacions on l'ús de memòria és una preocupació.
Aplicacions de Merge Sort:
- Ordenació de grans conjunts de dades
- Ordenació externa (quan el conjunt de dades és massa gran per cabre a la memòria)
- Recompte d'inversions (comptant el nombre d'inversions en una matriu)
- Trobar la mediana d'una matriu
Links ràpids:
- Articles recents sobre Merge Sort
- Top Ordenació de preguntes i problemes de l'entrevista
- Pràctica de problemes sobre algorisme d'ordenació
- Test sobre l'ordenació de combinacions
