Donades dues cordes, S1 i S2 , la tasca és trobar la longitud de la subseqüència comuna més llarga, és a dir, la subseqüència més llarga present a les dues cadenes.
nat vs llit
A subseqüència comuna més llarga (LCS) es defineix com la subseqüència més llarga que és comuna a totes les seqüències d'entrada donades.
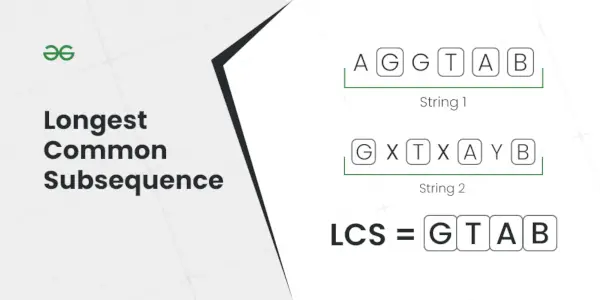
Subseqüència comuna més llarga
Exemples:
Pràctica recomanada Subseqüència comú més llarga Prova-ho!Entrada: S1 = ABC, S2 = ACD
Sortida: 2
Explicació: La subseqüència més llarga que està present en ambdues cadenes és AC.Entrada: S1 = AGGTAB, S2 = GXTXAYB
Sortida: 4
Explicació: La subseqüència comuna més llarga és GTAB.Entrada: S1 = ABC, S2 = CBA
Sortida: 1
Explicació: Hi ha tres subseqüències comunes de longitud 1, A, B i C i cap subseqüència comuna de longitud superior a 1.Entrada: S1 = XYZW, S2 = XYWZ
Sortida: 3
Explicació: Hi ha dues subseqüències comunes de longitud 3 XYZ, i XYW, i cap subseqüència comuna. de longitud superior a 3.
La subseqüència comuna més llarga (LCS) utilitzant la recursió:
Genereu totes les subseqüències possibles i trobeu la més llarga entre elles que estigui present en ambdues cadenes utilitzant Seguiu els passos següents per implementar la idea:
- Creeu una funció recursiva [per exemple lcs() ].
- Comproveu la relació entre els primers caràcters de les cadenes que encara no s'han processat.
- Depenent de la relació, crida a la següent funció recursiva tal com s'ha esmentat anteriorment.
- Retorna la longitud del LCS rebut com a resposta.
A continuació es mostra la implementació de l'enfocament recursiu:
C++C// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra>C#// A Naive recursive implementation // of LCS problem #include int max(int a, int b); // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int i, int j) // Utility function to get max of // 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a: b; } // Codi del controlador int main() { char S1[] = 'BD'; char S2[] = 'ABCD'; int m = strlen(S1); int n = strlen(S2); int i = 0, j = 0; // Crida a la funció printf('La longitud de LCS és %d', lcs(S1, S2, i, j)); retorn 0; }>>>Java>> PythonPHP// C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) if (m == 0 // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a: b; } // Codi del controlador public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Cadena S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Llargada; int n = S2.Llargada; Console.Write('La longitud de LCS és' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Aquest codi és aportat per Sam007>>>Javascriptb)? a: b; } var s1 = 'AGGTAB'; var s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; var X = s1; var Y = s2; var m = X.longitud; var n = Y.longitud; document.write('La longitud de LCS és' + ' ' + lcs( X, Y, m, n ) ); // Aquest codi aportat per umadevi9616>
SortidaLength of LCS is 4>Complexitat temporal: O (2m+n)
Espai auxiliar: O(1)S'utilitza la subseqüència comuna més llarga (LCS). Memoització :
1. Subestructura òptima:
Vegeu per resoldre l'estructura de L(X[0, 1, . . ., m-1], Y[0, 1, . . . , n-1]) estem prenent l'ajuda de les subestructures de X[0 , 1, …, m-2], Y[0, 1,…, n-2], segons la situació (és a dir, utilitzar-los de manera òptima) per trobar la solució del conjunt.
2. Subproblemes superposats:
Si utilitzem l'enfocament recursiu anterior per a les cadenes BD i ABCD , obtindrem un arbre de recursivitat parcial tal com es mostra a continuació. Aquí podem veure que el subproblema L(BD, ABCD) s'està calculant més d'una vegada. Si es considera l'arbre total, hi haurà diversos subproblemes superposats.
L(AXYT, AYZX)
/
L(AXY, AYZX) L(AXYT, AYZ)
/ /
L(AX, AYZX) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXYT, AY)Enfocament: A causa de la presència d'aquestes dues propietats podem utilitzar la programació dinàmica o la Memoization per resoldre el problema. A continuació es mostra l'enfocament de la solució mitjançant recursivitat.
- Crea una funció recursiva. També creeu una matriu 2D per emmagatzemar el resultat d'un estat únic.
- Durant la trucada de recursivitat, si el mateix estat es crida més d'una vegada, podem tornar directament la resposta emmagatzemada per a aquest estat en lloc de tornar a calcular.
A continuació es mostra la implementació de l'enfocament anterior:
C++Java// A Top-Down DP implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int m, int n, vector>& dp) { si (m == 0 || n == 0) retorna 0; si (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) retorna dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { retorna dp[m][n]; } retorna dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } // Codi del controlador int main() { char X[] = 'AGGTAB'; char Y[] = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = strlen(X); int n = strlen(Y); vector > dp(m + 1, vector (n + 1, -1)); cout<< 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp); return 0; }> Python/*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.*; class GFG { // A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n, int[][] dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (dp[m][n] != -1) return dp[m][n]; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) { dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); return dp[m][n]; } dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); return dp[m][n]; } // Drivers code public static void main(String args[]) { String X = 'AGGTAB'; String Y = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = X.length(); int n = Y.length(); int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) { dp[i][j] = -1; } } System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C## A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem # Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] def lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp): if (m == 0 or n == 0): return 0 if (dp[m][n] != -1): return dp[m][n] if X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]: dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp) return dp[m][n] dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)) return dp[m][n] # Driver code X = 'AGGTAB' Y = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(X) n = len(Y) dp = [[-1 for i in range(n + 1)]for j in range(m + 1)] print(f'Length of LCS is {lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)}') # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>Javascript/* C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */ using System; class GFG { /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ static int lcs(char[] X, char[] Y, int m, int n, int[, ] L) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (L[m, n] != -1) return L[m, n]; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) { L[m, n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, L); return L[m, n]; } L[m, n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, L), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, L)); return L[m, n]; } /* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */ static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a: b; } public static void Principal() { String s1 = 'AGGTAB'; String s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; char[] X = s1.ToCharArray(); char[] Y = s2.ToCharArray(); int m = X.Llargada; int n = Y.Llargada; int[, ] L = nou int[m + 1, n + 1]; per (int i = 0; i<= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { L[i, j] = -1; } } Console.Write('Length of LCS is' + ' ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, L)); } } // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>/* A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem */ /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ function lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } /* Driver code */ let X = 'AGGTAB'; let Y = 'GXTXAYB'; let m = X.length; let n = Y.length; let dp = new Array(m + 1); for(let i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { dp[i] = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1); } console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>
SortidaLength of LCS is 4>Complexitat temporal: O(m * n) on m i n són les longituds de les cordes.
Espai auxiliar: O(m * n) Aquí s'ignora l'espai recursiu de la pila.Subseqüència comuna més llarga (LCS) utilitzant Bottom-Up (tabulació):
Podem utilitzar els passos següents per implementar l'enfocament de programació dinàmica per a LCS.
desviació estàndard numpy
- Creeu una matriu 2D dp[][] amb files i columnes iguals a la longitud de cada cadena d'entrada més 1 [el nombre de files indica els índexs de S1 i les columnes indiquen els índexs de S2 ].
- Inicieu la primera fila i columna de la matriu dp a 0.
- Itera per les files de la matriu dp, començant per 1 (per exemple, utilitzant l'iterador i ).
- Per cadascú i , itera totes les columnes des de j = 1 a n :
- Si S1[i-1] és igual a S2[j-1] , establiu l'element actual de la matriu dp al valor de l'element a ( dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 ).
- En cas contrari, establiu l'element actual de la matriu dp al valor màxim de dp[i-1][j] i dp[i][j-1] .
- Després dels bucles imbricats, l'últim element de la matriu dp contindrà la longitud del LCS.
Vegeu la il·lustració següent per a una millor comprensió:
Il·lustració:
Digues que les cordes ho són S1 = AGGTAB i S2 = GXTXAYB .
Primer pas: Creeu inicialment una matriu 2D (per exemple, dp[][]) de mida 8 x 7 la primera fila i la primera columna de la qual s'omplen amb 0.
Creació de la taula dp
Segon pas: Travessa per i = 1. Quan j esdevé 5, S1[0] i S2[4] són iguals. Així, el dp[][] s'actualitza. Per als altres elements prenem el màxim de dp[i-1][j] i dp[i][j-1]. (En aquest cas, si tots dos valors són iguals, hem utilitzat fletxes per a les files anteriors).
Omplint la fila no 1
Tercer pas: Mentre es travessa per i = 2, S1[1] i S2[0] són iguals (tots dos són 'G'). Així, el valor dp d'aquesta cel·la s'actualitza. La resta d'elements s'actualitzen segons les condicions.
Omplint la fila núm. 2
Quart pas: Per a i = 3, S1[2] i S2[0] tornen a ser iguals. Les actualitzacions són les següents.
Fila d'ompliment núm. 3
Cinquè pas: Per a i = 4, podem veure que S1[3] i S2[2] són iguals. Així, dp[4][3] s'ha actualitzat com a dp[3][2] + 1 = 2.
Omplint la fila 4
Sisè pas: Aquí podem veure que per a i = 5 i j = 5 els valors de S1[4] i S2[4] són els mateixos (és a dir, tots dos són 'A'). Així, dp[5][5] s'actualitza en conseqüència i es converteix en 3.
Omplint la fila 5
Pas final: Per a i = 6, vegeu que els últims caràcters de les dues cadenes són iguals (són 'B'). Per tant, el valor de dp[6][7] es converteix en 4.
llocs com ara bedpageOmplint l'última fila
Així obtenim la longitud màxima de la subseqüència comuna com 4 .
A continuació es mostra una implementació tabulada per al problema LCS.
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) { // Initializing a matrix of size // (m+1)*(n+1) int L[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. Note that // L[i][j] contains length of LCS of // X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) if (i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains length of LCS // for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n]; } // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; }>C#// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int L[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up // fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS // of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X.charAt(i - 1) == Y.charAt(j - 1)) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } return L[m][n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a: b; } public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence (); Cadena S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Cadena S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.longitud(); int n = S2.longitud(); System.out.println('La longitud de LCS és' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Aquest codi és aportat per Saket Kumar>>>PythonPHP// Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int[, ] L = new int[m + 1, n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. // Note that L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i, j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i, j] = L[i - 1, j - 1] + 1; else L[i, j] = max(L[i - 1, j], L[i, j - 1]); } return L[m, n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a: b; } // Codi del controlador public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Cadena S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Llargada; int n = S2.Llargada; Console.Write('La longitud de LCS és' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Aquest codi és aportat per Sam007>>>Javascript// Dynamic Programming C# // implementation of LCS problem function lcs($X , $Y, $m, $n) { // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion . // Note: L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for ($i = 0; $i <= $m; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j <= $n; $j++) if ($i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains the length of // LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return $L[$m][$n]; } // Driver Code $S1 = 'AGGTAB'; $S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; $m = strlen($S1); $n = strlen($S2) ; echo 'Length of LCS is '; echo lcs($S1, $S2, $m, $n); // This code is contributed // by Shivi_Aggarwal ?>>
SortidaLength of LCS is 4>Complexitat temporal: O(m * n), que és molt millor que la complexitat temporal del pitjor dels casos de la implementació recursiva ingènua.
Espai auxiliar: O(m * n) perquè l'algorisme utilitza una matriu de mida (m+1)*(n+1) per emmagatzemar la longitud de les subcadenes comunes.La subseqüència comuna més llarga (LCS) mitjançant Bottom-Up (optimització de l'espai):
- En l'enfocament de tabulació anterior, estem utilitzant L[i-1][j] i L[i][j], etc., aquí L[i-1] es refereix a la fila anterior de la matriu L i L[i] es refereix a la fila actual.
- Podem fer l'optimització de l'espai utilitzant dos vectors un és anterior i un altre és actual.
- Quan surt el bucle for interior, estem inicialitzant l'anterior igual al corrent.
A continuació es mostra la implementació:
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; int longestCommonSubsequence(string& text1, string& text2) { int n = text1.size(); int m = text2.size(); // initializing 2 vectors of size m vectorprev(m + 1, 0), cur(m + 1, 0); per (int idx2 = 0; idx2< m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2); return 0; }> Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.Arrays; public class GFG { public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(); int m = text2.length(); // Initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If matching if (text1.charAt(idx1 - 1) == text2.charAt(idx2 - 1)) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // Not matching else cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = Arrays.copyOf(cur, m + 1); } return cur[m]; } public static void main(String[] args) { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; String S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>C#def longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2): n = len(text1) m = len(text2) # Initializing two lists of size m prev = [0] * (m + 1) cur = [0] * (m + 1) for idx1 in range(1, n + 1): for idx2 in range(1, m + 1): # If characters are matching if text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]: cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1] else: # If characters are not matching cur[idx2] = max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]) prev = cur.copy() return cur[m] if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' # Function call print('Length of LCS is', longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)) # This code is contributed by Rishabh Mathur>Javascriptusing System; class Program { static int LongestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n = text1.Length; int m = text2.Length; // initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + Math.Max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } static void Main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call Console.WriteLine('Length of LCS is ' + LongestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>function longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2) { const n = text1.length; const m = text2.length; // Initializing two arrays of size m let prev = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); let cur = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); for (let idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { cur[idx2] = 0; } for (let idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (let idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If characters match if (text1[idx1 - 1] === text2[idx2 - 1]) { cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; } // If characters don't match else { cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } } // Update the 'prev' array prev = [...cur]; } return cur[m]; } // Main function function main() { const S1 = 'AGGTAB'; const S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call console.log('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } // Call the main function main();>
SortidaLength of LCS is 4>Complexitat temporal: O(m * n), que es manté igual.
Espai auxiliar: O(m) perquè l'algorisme utilitza dues matrius de mida m.







