L'alçada o la profunditat d'un arbre binari es pot definir com el nombre màxim o més gran d'arestes des d'un node fulla fins al node arrel o node arrel fins al node fulla. El node arrel estarà al nivell zero, això vol dir que si el node arrel no té cap dels nodes fills connectats, es diu que l'alçada o la profunditat de l'arbre binari particular és zero.
Prenguem un exemple per entendre millor l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
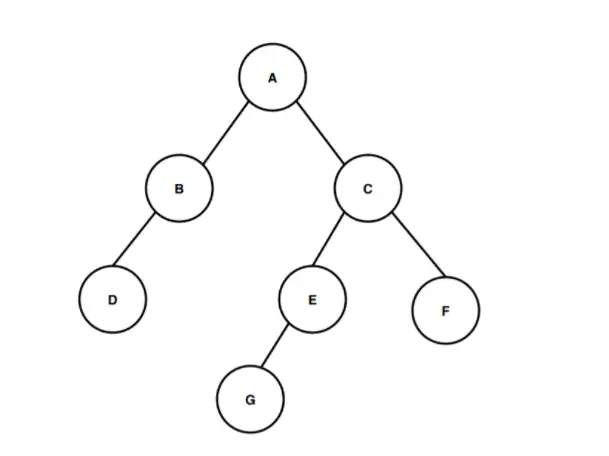
A la imatge de dalt, tenim un arbre binari que comença des del node arrel anomenat A. El node arrel A té dos nodes secundaris B i C com a fill esquerre i fill dret respectivament. I de la mateixa manera, el node fill esquerre B només té un node fill esquerre anomenat D i el node fill dret C té dos nodes fills E i F dels quals el node E té el node G com a únic fill esquerre.
mètodes de llista de matrius
Ara calculem l'alçada d'aquest arbre binari. Compteu el nombre d'arestes des del node arrel fins al node full més profund per calcular l'alçada de l'arbre binari. El node més profund que està present en aquest arbre binari és el node G. Per tant, per al càlcul de l'alçada o la profunditat d'aquest arbre binari hem de calcular el nombre d'arestes entre el node arrel i el node més profund G. La primera aresta és del node A al node C, la segona vora és del node C al node E i la tercera vora és del node E al node G. Per tant, per travessar des del node arrel A fins al node G més profund hi ha tres arestes. , de manera que l'alçada o profunditat de l'arbre binari és 3. El camí que hem seguit per passar de l'arrel al node de fulla més profund és A > C > E > G i aquest camí cobreix tres arestes durant el recorregut, per això segons a la definició de l'alçada de l'arbre binari, l'alçada d'aquest arbre binari és 3.
Maneres de trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari
Ara, escrivim codi per trobar l'alçada d'un arbre binari. Hi ha dues maneres de trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari. Un és el mètode recursiu i l'altre és el mètode no recursiu que farà servir l'estructura de dades de la cua per calcular l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
Via recursiva
Primer, vegem la manera recursiva de trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
Codi:
// Java program to create and to find the height of a binary tree by recursive way // util package is imported to use classes like Queue and LinkedList import java.util.*; // A class named Node is created representing a single node of a binary tree class Node{ // The class Node has three class variables named key and left and right of int type and Node type respectively. // the key variable holds the actual value that is assigned to that node of the binary tree int key; // left and right variables that are of Node type will be used to store the left and right child nodes of the parent of the binary tree Node left, right; // a parameterized constructor is created to create and add data to the node at the same time. public Node(int item) { key = item; left = right = null; } } // end of node class definition // A public class named BinaryTree is created having two constructors and methods to print the binary tree level-wise. class BinaryTree{ // A static variable named root_node is created that will represent the node of the binary tree static Node root_node; // A parametrized constructor of the BinaryTree class is written having the key as a parameter BinaryTree(int key) { // here we are constructing a new node and assigning it to the root node root_node = new Node(key); } BinaryTree() { root_node = null; } // a public static function named print tree is created to print all the nodes in the tree level-wise starting from the root node public static void printTree() { int h = height(root_node); int i; for (i=1; i<=h; i++){ printcurrentlevel(root_node, i); system.out.println(); } a public static function named height is created to fund the of binary tree starting from root node deepest leaf that present in passed as parameter called recursively until returned null find int height(node root){ then will be zero if (root="=" null) return 0; else { * compute each subtree lheight="height(root.left);" rheight="height(root.right);" use larger one both sub trees calcualted and which higher used. (lheight> rheight) return(lheight+1); else return(rheight+1); } } // a Public static function named printCurrentLevel is created to print al the nodes that are present in that level // this function is called repeatedly for each level of the binary tree to print all the nodes in that particular level public static void printCurrentLevel (Node root ,int level) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) System.out.print(root.key + ' '); else if (level > 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1); } } //the main function is created to create an object of the BinaryTree class and call the printTree method to level-wise print the nodes of the binary tree and the height method to find the height of the binary tree public static void main(String[] args){ // first of all we have created an Object of the BinaryTree class that will represent the binary tree BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); // now a new node with the value as 150 is added as the root node to the Binary Tree tree.root_node = new Node(150); // now a new node with the value 250 is added as a left child to the root node tree.root_node.left = new Node(250); // now a new node with the value 270 is added as a right child to the root node tree.root_node.right = new Node(270); // now a new node with the value 320 is added as a left child to the left node of the previous level node tree.root_node.left.left = new Node(320); // now a new node with the value 350 is added as a right child to the right node of the previous level node tree.root_node.left.right = new Node(350); /* 150 / 250 270 / / 320 350 null null */ System.out.println('Printing the nodes of tree level wise :'); System.out.println('Level order traversal : '); tree.printTree(); // height of the binary tree is calculated bypassing the root as parameter to the height() function. int h = tree.height(tree.root_node) System.out.println('The height of the Binary tree is : ' + h ); } } // end of the BinaryTree class </=h;> Sortida: La sortida del codi anterior és:
Printing the nodes of tree level wise: Level order traversal: (level 0) 150 (level 1) 250 270 (level 2) 320 350 The height of the Binary tree is: 2
De manera recursiva, hem anomenat el alçada () funcionen repetidament per trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari. El node arrel de l'arbre binari es passa com a paràmetre a la funció height(). La funció height() calcula l'alçada dels dos subarbres del node arrel i quina de les dues altures és més alta es considera com l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
Via no recursiva
Vegem ara la manera no recursiva de trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
Codi:
// A C++ program to create and to find the height of a binary tree by non recursive way // iostream header file is included to use the cin and cout objects of the istream and ostream classes respectively #include #include using namespace std; // A struct named Node is created representing a single node of a binary tree struct Node { // The struct Node has three variables named key and left and right of int type and Node type respectively. // the key variable holds the actual value that is assigned to that node of the binary tree int key; // left and right variables that are of Node type will be used to store the left and right child nodes of the parent of the binary tree struct Node* left, *right; }; // A Function named newNode is created to add a new node to the binary tree, the newNode function has one parameter of integer type named key that will represent the value that particular new node will be storing Node* newNode(int key) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->key = key; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; return (temp); } // A function named height is created to find the height of the binary tree with non recursive way // The parameter to the height function is the root node of the binary tree that will be present at level zero // In the height function the nodes of the binary tree are added into the Queue data structure and the depth variable is incremented until // the NULL node is encountered while traversing the nodes of the binary tree stored in the Queue data structure. int height(struct Node* root){ //Initialising a variable to count the //height of tree int depth = 0; queueq; //Pushing first level element along with NULL q.push(root); q.push(NULL); while(!q.empty()){ Node* temp = q.front(); q.pop(); //When NULL encountered, increment the value if(temp == NULL){ depth++; } //If NULL not encountered, keep moving if(temp != NULL){ if(temp->left){ q.push(temp->left); } if(temp->right){ q.push(temp->right); } } //If queue still have elements left, //push NULL again to the queue. else if(!q.empty()){ q.push(NULL); } } return depth; } // Start of the main function int main() { // first of all we have created an Object of the struct Node that will represent the binary tree // the value of the root node is 10 Node *root = newNode(10); // now a new node with the value 20 is added as a left child to the root node root->left = newNode(20); // now a new node with the value 30 is added as a right child to the root node root->right = newNode(30); // now a new node with the value 40 is added as a left child to the left node of the previous level node root->left->left = newNode(40); // now a new node with the value 50 is added as a right child to the left node of the previous level node root->left->right = newNode(50); /* 10 / 20 30 / / 40 50 null null */ cout<<'the height(depth) of tree is: '<<height(root); cout<<endl; } end the main function < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> The Height(Depth) of the tree is: 2 </pre> <p>In this approach, we have used a non recursive way to find the depth of the binary tree. To find the height of the binary tree, we have written a function named height that will require a parameter of Node type (that means the root of the binary tree whose height needs to be calculated). The root of the binary tree is present at level zero, which means the height or depth of the root is zero.</p> <p>In the non recursive approach, we use the Queue Data Structure to find the depth of the binary tree. The nodes of the binary tree for which we want to find the depth are added to the Queue data structure with the help of an enqueue operation to which the node of the binary tree is passed as a parameter to this function.</p> <p>Once all the nodes are added to the queue, the nodes added in the queue are removed by calling the dequeue function that will keep on removing one element from the queue until the null node of the binary tree is encountered. Each time a node of the binary tree from the queue is removed, the depth variable representing the depth of the binary tree is incremented by one. And in the end, the value of the depth variable will represent the final depth of the binary tree.</p> <hr></'the> En aquest enfocament, hem utilitzat una manera no recursiva per trobar la profunditat de l'arbre binari. Per trobar l'alçada de l'arbre binari, hem escrit una funció anomenada alçada que requerirà un paràmetre de tipus Node (és a dir, l'arrel de l'arbre binari l'alçada del qual s'ha de calcular). L'arrel de l'arbre binari està present al nivell zero, el que significa que l'alçada o la profunditat de l'arrel és zero.
En l'enfocament no recursiu, utilitzem l'estructura de dades de la cua per trobar la profunditat de l'arbre binari. Els nodes de l'arbre binari dels quals volem trobar la profunditat s'afegeixen a l'estructura de dades de la cua amb l'ajuda d'una operació de cua a la qual es passa el node de l'arbre binari com a paràmetre d'aquesta funció.
descarregar vídeos de youtube vlc
Un cop s'afegeixen tots els nodes a la cua, els nodes afegits a la cua s'eliminen cridant a la funció de descua, que continuarà eliminant un element de la cua fins que es trobi el node nul de l'arbre binari. Cada vegada que s'elimina un node de l'arbre binari de la cua, la variable de profunditat que representa la profunditat de l'arbre binari s'incrementa en un. I al final, el valor de la variable de profunditat representarà la profunditat final de l'arbre binari.
