Arbre binari és una estructura de dades no lineal de tipus arbre que s'utilitzen principalment per ordenar i cercar perquè emmagatzemen dades en forma jeràrquica. En aquesta secció, aprendrem el implementació de l'estructura de dades d'arbre binari a Java . A més, ofereix una breu descripció de l'estructura de dades d'arbre binari.
Arbre binari
Un arbre en què cada node (pare) té com a màxim dos nodes secundaris (esquerra i dreta) s'anomena arbre binari. El node més superior s'anomena node arrel. En un arbre binari, un node conté les dades i el punter (adreça) del node fill esquerre i dret.
El alçada d'un arbre binari és el nombre de vores entre l'arrel de l'arbre i la seva fulla més llunyana (més profunda). Si l'arbre és buit , l'alçada és 0 . L'alçada del node es denota amb h .
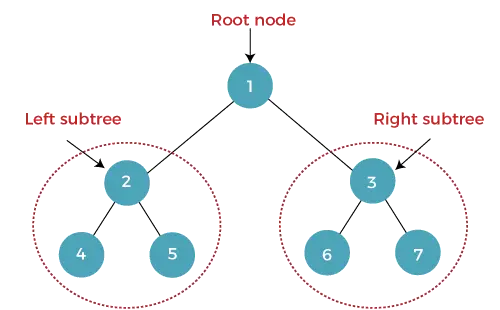
L'alçada de l'arbre binari anterior és 2.
Podem calcular el nombre de fulles i nodes utilitzant la fórmula següent.
- El nombre màxim de nodes de fulla és un arbre binari: 2h
- El nombre màxim de nodes és un arbre binari: 2h+1-1
On, h és l'alçada de l'arbre binari.
Exemple d'arbre binari

Tipus d'arbre binari
Hi ha els següents tipus d'arbre binari a l'estructura de dades:
- Arbre complet / estrictament binari
- Arbre binari complet
- Arbre binari perfecte
- Arbre binari d'equilibri
- Arbre binari arrelat
- Arbre binari degenerat/ patològic
- Arbre binari estès
- Arbre binari esbiaixat
- Arbre binari esbiaixat a l'esquerra
- Arbre binari esbiaixat a la dreta
- Arbre binari roscat
- Arbre binari d'un sol fil
- Arbre binari de doble fil
Implementació d'arbres binaris a Java
Hi ha moltes maneres d'implementar l'arbre binari. En aquesta secció, implementarem l'arbre binari mitjançant l'estructura de dades LinkedList. Juntament amb això, també implementarem les ordres de recorregut, cercant un node i inserint un node en un arbre binari.
Implementació de l'arbre binari mitjançant LinkedList
Algorisme
Definiu la classe Node que conté tres atributs, a saber: dades esquerra i dreta. Aquí, l'esquerra representa el fill esquerre del node i la dreta representa el fill dret del node.
- Quan es crea un node, les dades passaran a l'atribut de dades del node i tant l'esquerra com la dreta es posaran a nul.
- Definiu una altra classe que tingui una arrel d'atribut.
- L'arrel representa el node arrel de l'arbre i l'inicializa a nul.
- Comprova si l'arrel és nul·la, la qual cosa significa que l'arbre està buit. Afegirà el nou node com a root.
- En cas contrari, afegirà root a la cua.
- El node variable representa el node actual.
- Primer, comprova si un node té un fill esquerre i dret. En cas afirmatiu, afegirà els dos nodes a la cua.
- Si el fill esquerre no està present, afegirà el nou node com a fill esquerre.
- Si l'esquerra està present, afegirà el nou node com a fill dret.
- Travessa tot l'arbre i després imprimeix el fill esquerre seguit de l'arrel i després el fill dret.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Sortida:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Operacions d'arbre binari
En un arbre binari es poden realitzar les operacions següents:
arquitectura rusc
- Inserció
- Supressió
- Cerca
- Travessia
Programa Java per inserir un node a l'arbre binari
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Sortida:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Programa Java per eliminar un node a Java
Algorisme
- Començant per l'arrel, cerqueu el node més profund i més a la dreta de l'arbre binari i el node que volem suprimir.
- Substituïu les dades del node més profund a la dreta pel node que cal suprimir.
- A continuació, suprimiu el node més profund més a la dreta.
Considereu la figura següent.

DeleteNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Sortida:
va dir Madhuri
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Programa Java per cercar un node a l'arbre binari
Algorisme
- Definiu la classe Node que té tres atributs, a saber: dades esquerra i dreta. Aquí, l'esquerra representa el fill esquerre del node i la dreta representa el fill dret del node.
- Quan es crea un node, les dades passaran a l'atribut de dades del node i tant l'esquerra com la dreta es posaran a nul.
- Definiu una altra classe que tingui dos atributs arrel i bandera.
- L'arrel representa el node arrel de l'arbre i l'inicia a nul.
- La bandera s'utilitzarà per comprovar si el node donat està present a l'arbre o no. Inicialment, s'establirà com a fals.
- Comprova si l'arrel és nul·la, la qual cosa significa que l'arbre està buit.
- Si l'arbre no està buit, compararà les dades temporals amb el valor. Si són iguals, establirà la bandera com a vertader i tornarà.
- Travessa el subarbre esquerre trucant a searchNode() de manera recursiva i comproveu si el valor està present al subarbre esquerre.
- Travessa el subarbre dret cridant a searchNode() de manera recursiva i comproveu si el valor està present al subarbre dret.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Sortida:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Travessia d'arbre binari
| Ordre transversal | Primera visita | Segona visita | Tercera visita |
|---|---|---|---|
| En ordre | Visiteu el subarbre esquerre en ordre | Visiteu el node arrel | Visiteu el subarbre dret en ordre |
| Comanda prèvia | Visiteu el node arrel | Visiteu el subarbre esquerre en preordre | Visiteu el subarbre dret en comanda prèvia |
| Comandes per correu | Visiteu el subarbre esquerre en postordre | Visiteu el subarbre dret en postordre | Visiteu el node arrel |
Nota: Excepte els tres recorreguts anteriors, hi ha un altre ordre de recorregut que s'anomena travessa de límits.
Programa Java per travessar en ordre, pre-ordre i post-ordre
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Sortida:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
A més de les operacions anteriors, també podem realitzar les operacions com ara el node gran, el node més petit i la suma de tots els nodes.
Programa Java per trobar el node més gran de l'arbre binari
LargestNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Sortida:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Programa Java per trobar el node més petit a l'arbre binari
Algorisme
- Definiu la classe Node que té tres atributs, a saber: dades, esquerra i dreta. Aquí, l'esquerra representa el fill esquerre del node i la dreta representa el fill dret del node.
- Quan es crea un node, les dades passaran a l'atribut de dades del node i tant l'esquerra com la dreta es definiran com a nul.
- Definiu una altra classe que tingui una arrel d'atribut.
Arrel representar el node arrel de l'arbre i inicialitzar-lo a nul.
- Comprova si arrel és nul·la , que vol dir que l'arbre està buit.
- Si l'arbre no està buit, definiu una variable min que emmagatzemarà les dades temporals.
- Esbrineu el node mínim del subarbre esquerre cridant a smallestElement() de manera recursiva. Emmagatzema aquest valor a leftMin. Compareu el valor de min amb leftMin i emmagatzemeu el mínim de dos a min.
- Esbrineu el node mínim del subarbre dret cridant a smallestElement() de manera recursiva. Emmagatzema aquest valor a rightMin. Compareu el valor de min amb rightMin i emmagatzemeu el màxim de dos a min.
- Al final, min mantindrà el node més petit de l'arbre binari.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Sortida:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Programa Java per trobar l'amplada màxima d'un arbre binari
Algorisme
- Definiu la classe Node que té tres atributs, a saber: dades esquerra i dreta. Aquí, l'esquerra representa el fill esquerre del node i la dreta representa el fill dret del node.
- Quan es crea un node, les dades passaran a l'atribut de dades del node i tant l'esquerra com la dreta es posaran a nul.
- Definiu una altra classe que tingui una arrel d'atribut.
Arrel representa el node arrel de l'arbre i l'inicia a nul.
- La variable maxWidth emmagatzemarà el nombre màxim de nodes presents a qualsevol nivell.
- La cua s'utilitza per recórrer l'arbre binari a nivell.
- Comprova si l'arrel és nul·la, la qual cosa significa que l'arbre està buit.
- Si no, afegiu el node arrel a la cua. La variable nodesInLevel fa un seguiment del nombre de nodes a cada nivell.
- Si nodesInLevel > 0, traieu el node de la part davantera de la cua i afegiu el seu fill esquerre i dret a la cua. Per a la primera iteració, s'eliminarà el node 1 i els seus nodes secundaris 2 i 3 s'afegiran a la cua. A la segona iteració, s'eliminarà el node 2, els seus fills 4 i 5 s'afegiran a la cua, etc.
- MaxWidth emmagatzemarà max (maxWidth, nodesInLevel). Per tant, en qualsevol moment donat, representarà el nombre màxim de nodes.
- Això continuarà fins que es travessen tots els nivells de l'arbre.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Sortida:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
