NumPy significa Numerical Python. És una biblioteca de Python utilitzada per treballar amb una matriu. A Python, fem servir la llista per a la matriu, però és lent de processar. La matriu NumPy és un objecte de matriu N-dimensional potent i s'utilitza en àlgebra lineal, transformada de Fourier i capacitats de nombres aleatoris. Proporciona un objecte matriu molt més ràpid que les llistes tradicionals de Python.
Tipus de matriu:
- Matriu unidimensional
- Matriu multidimensional
Matriu unidimensional:
Una matriu unidimensional és un tipus de matriu lineal.

Matriu unidimensional
Exemple:
Python 3 # importing numpy module import numpy as np # creating list list = [1, 2, 3, 4] # creating numpy array sample_array = np.array(list) print('List in python : ', list) print('Numpy Array in python :', sample_array)>
Sortida:
List in python : [1, 2, 3, 4] Numpy Array in python : [1 2 3 4]>
Comproveu el tipus de dades per a la llista i la matriu:
Python 3 print(type(list_1)) print(type(sample_array))>
Sortida:
>
Matriu multidimensional:
Les dades en matrius multidimensionals s'emmagatzemen en forma tabular.
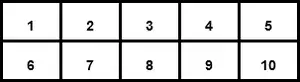
Matriu bidimensional
Exemple:
Python 3 # importing numpy module import numpy as np # creating list list_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] list_2 = [5, 6, 7, 8] list_3 = [9, 10, 11, 12] # creating numpy array sample_array = np.array([list_1, list_2, list_3]) print('Numpy multi dimensional array in python
', sample_array)> Sortida:
Numpy multi dimensional array in python [[ 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8] [ 9 10 11 12]]>
Nota: utilitzar [ ] operadors dins de numpy.array() per a multidimensionals
Anatomia d'una matriu:
1. Eix: L'eix d'una matriu descriu l'ordre de la indexació a la matriu.
Eix 0 = unidimensional
bucle del programa javaEix 1 = Bidimensional
Eix 2 = Tridimensional
2. Forma: El nombre d'elements juntament amb cada eix. És d'una tupla.
Exemple:
Python 3 # importing numpy module import numpy as np # creating list list_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] list_2 = [5, 6, 7, 8] list_3 = [9, 10, 11, 12] # creating numpy array sample_array = np.array([list_1, list_2, list_3]) print('Numpy array :') print(sample_array) # print shape of the array print('Shape of the array :', sample_array.shape)> Sortida:
Numpy array : [[ 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8] [ 9 10 11 12]] Shape of the array : (3, 4)>
Exemple:
Python 3 import numpy as np sample_array = np.array([[0, 4, 2], [3, 4, 5], [23, 4, 5], [2, 34, 5], [5, 6, 7]]) print('shape of the array :', sample_array.shape)> Sortida:
shape of the array : (5, 3)>
3. Classificació: El rang d'una matriu és simplement el nombre d'eixos (o dimensions) que té.
La matriu unidimensional té el rang 1.

Classificació 1
La matriu bidimensional té el rang 2.

Rang 2
4. Objectes de tipus de dades (dtype): Objectes de tipus de dades (dtype) és una instància de numpy.dtype classe. Descriu com s'han d'interpretar els bytes del bloc de memòria de mida fixa corresponent a un element de matriu.
Exemple:
Python 3 # Import module import numpy as np # Creating the array sample_array_1 = np.array([[0, 4, 2]]) sample_array_2 = np.array([0.2, 0.4, 2.4]) # display data type print('Data type of the array 1 :', sample_array_1.dtype) print('Data type of array 2 :', sample_array_2.dtype)> Sortida:
Data type of the array 1 : int32 Data type of array 2 : float64>
Alguna manera diferent de crear Numpy Array:
1. numpy.array() : L'objecte de matriu Numpy a Numpy s'anomena ndarray. Podem crear ndarray utilitzant numpy.array() funció.
Sintaxi: numpy.array(paràmetre)
Exemple:
Python 3 # import module import numpy as np #creating a array arr = np.array([3,4,5,5]) print('Array :',arr)> Sortida:
Array : [3 4 5 5]>
2. numpy.friter() : La funció fromiter() crea una nova matriu unidimensional a partir d'un objecte iterable.
Sintaxi: numpy.friter(iterable, dtype, count=-1)
Exemple 1:
Python 3 #Import numpy module import numpy as np # iterable iterable = (a*a for a in range(8)) arr = np.fromiter(iterable, float) print('fromiter() array :',arr)> Sortida:
matriu fromiter(): [ 0. 1. 4. 9. 16. 25. 36. 49.]
Exemple 2:
Python 3 import numpy as np var = 'Geekforgeeks' arr = np.fromiter(var, dtype = 'U2') print('fromiter() array :', arr)> Sortida:
matriu fromiter(): [‘G’ ‘e’ ‘e’ ‘k’ ‘f’ ‘o’ ‘r’ ‘g’ ‘e’ ‘e’ ‘k’ ‘s’]
3. numpy.arange() : Aquesta és una funció NumPy integrada que retorna valors uniformement espaiats dins d'un interval determinat.
Sintaxi: numpy.arange([inici, ]stop, [pas, ]dtype=Cap)
Exemple:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.arange(1, 20 , 2, dtype = np.float32)>
Sortida:
matriu([ 1., 3., 5., 7., 9., 11., 13., 15., 17., 19.], dtype=float32)
4. numpy.linspace() : Aquesta funció retorna nombres espaiats uniformement sobre un determinat entre dos límits.
Sintaxi: numpy.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None, axis=0)
Exemple 1:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.linspace(3.5, 10, 3)>
Sortida:
array([ 3.5 , 6.75, 10. ])>
Exemple 2:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.linspace(3.5, 10, 3, dtype = np.int32)>
Sortida:
array([ 3, 6, 10])>
5. numpy.empty() : Aquesta funció crea una nova matriu de forma i tipus donats, sense inicialitzar el valor.
Sintaxi: numpy.empty (forma, dtype=float, ordre='C')
Exemple:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.empty([4, 3], dtype = np.int32, order = 'f')>
Sortida:
array([[ 1, 5, 9], [ 2, 6, 10], [ 3, 7, 11], [ 4, 8, 12]])>
6. numpy.ones(): Aquesta funció s'utilitza per obtenir una nova matriu de forma i tipus donats, plena d'uns (1).
Sintaxi: numpy.ones (forma, dtype=Cap, ordre='C')
Exemple:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.ones([4, 3], dtype = np.int32, order = 'f')>
Sortida:
array([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]])>
7. numpy.zeros() : Aquesta funció s'utilitza per obtenir una nova matriu de forma i tipus determinats, plena de zeros (0).
Sintaxi: numpy.ones(forma, dtype=Cap)
Exemple:
Python 3 import numpy as np np.zeros([4, 3], dtype = np.int32, order = 'f')>
Sortida:
array([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]])>
